Driving with arthritis pain: Stay comfortable — and safe — behind the wheel

Daily cup of coffee may prevent afib recurrence

Gene-editing therapy lowers harmful blood fats in early study

What is EMDR therapy, and who can it help?

GLP-1 drugs versus bariatric surgery for treating obesity

Two dumbbells, three exercises, and 10 minutes

Easing the emotional burden of IBS

Modify your push-ups to meet your fitness level

What is long QT syndrome?

Stroke survivors may benefit from very low LDL levels
Breast Cancer Archive
Articles
Can a high-fiber diet reduce your risk of breast cancer?
Research we're watching
Your diet may influence your breast cancer risk. An analysis of 20 studies by researchers from the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, which was published online April 6, 2020, by the journal Cancer, found that women who ate the most fiber were 8% less likely to go on to develop breast cancer compared with the women who ate the least.
The reduction in breast cancer risk was seen for both premenopausal and postmenopausal breast cancers, as well as different types of breast cancer, including those that were estrogen and progesterone receptor–positive and estrogen and progesterone receptor–negative. Researchers from the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health said that that the reduction may be due to fiber's effect in reducing both blood sugar and estrogen levels in the body.
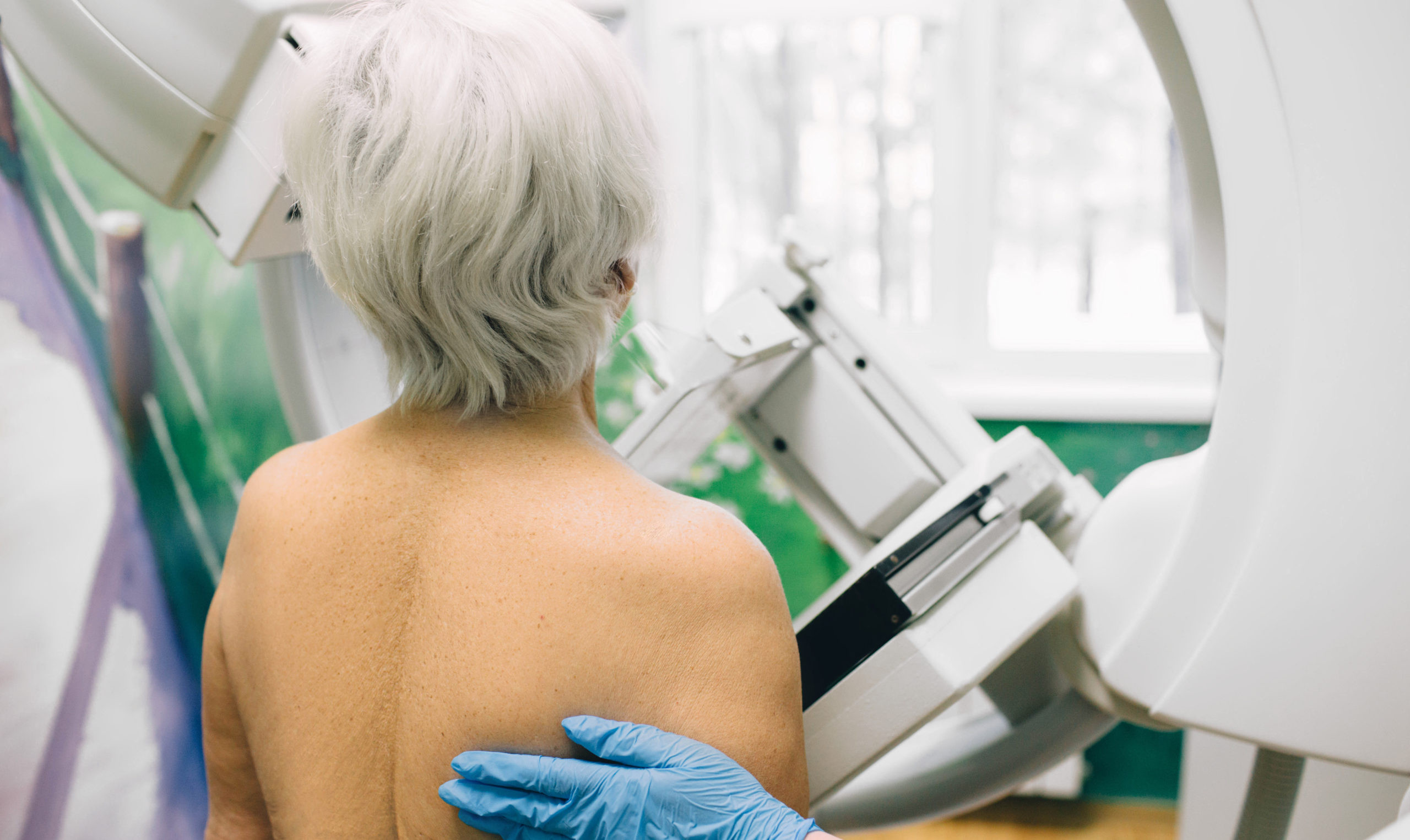
Are you old enough to give up your screening mammogram?
There's no easy answer to this question. Rather, women should make the decision based on their individual needs.
Most women don't look forward to their routine mammogram, which can be uncomfortable and stressful. You may wonder: Is there an age when can you dispense with this regular chore? 75, 80, 85?
The truth is that experts haven't determined a magic age when women no longer need breast cancer screening — largely because scientific evidence in this area is lacking, says Dr. Kathryn Rexrode, associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and chief of the Division of Women's Health at Brigham and Women's Hospital. But many experts also agree that continuing mammography might not be the right choice beyond age 75. The real question, they say, is what is the right age for you to stop based on your individual needs? To decide, you need to understand both the potential risks and benefits of breast cancer screening.
Cancer death rates continue to decline
Research we're watching
According to a report published March 12 in the journal Cancer, the rate of death from cancer has continued to decline in the United States, dropping on average 1.5% a year from 2001 to 2017. The decline showed up for all ethnic and age groups between 2013 and 2017. The findings were based on cancer incidence data collected by the CDC and the National Cancer Institute.
But not all news was good: the number of new cancer diagnoses in women rose slightly during 2012 to 2016. A more detailed look at cancer deaths among women found a drop in cancer deaths for a majority of the most common cancers, including breast cancer, melanoma, lung cancer, and colorectal cancer. But deaths in women increased when it came to uterine, brain, liver, heart, and pancreatic cancer.
Is it time to give up your annual mammogram?
The question of what age a woman can stop having mammograms does not have a definite answer, but is one each woman must answer based on her circumstances and her feelings about the risks of the procedure versus its benefits.
Toxic beauty
Are your personal care products putting your health at risk?
The average woman uses 12 different beauty products every day — cleansers, conditioners, hair dyes, fragrances, skin care products, scented lotions, nail polish, and makeup, to name a few. Take a quick glance at the labels, and you'll see a cocktail of chemical components.
You might assume that all these ingredients have been tested to ensure that they're safe for long-term use. That's not the case.
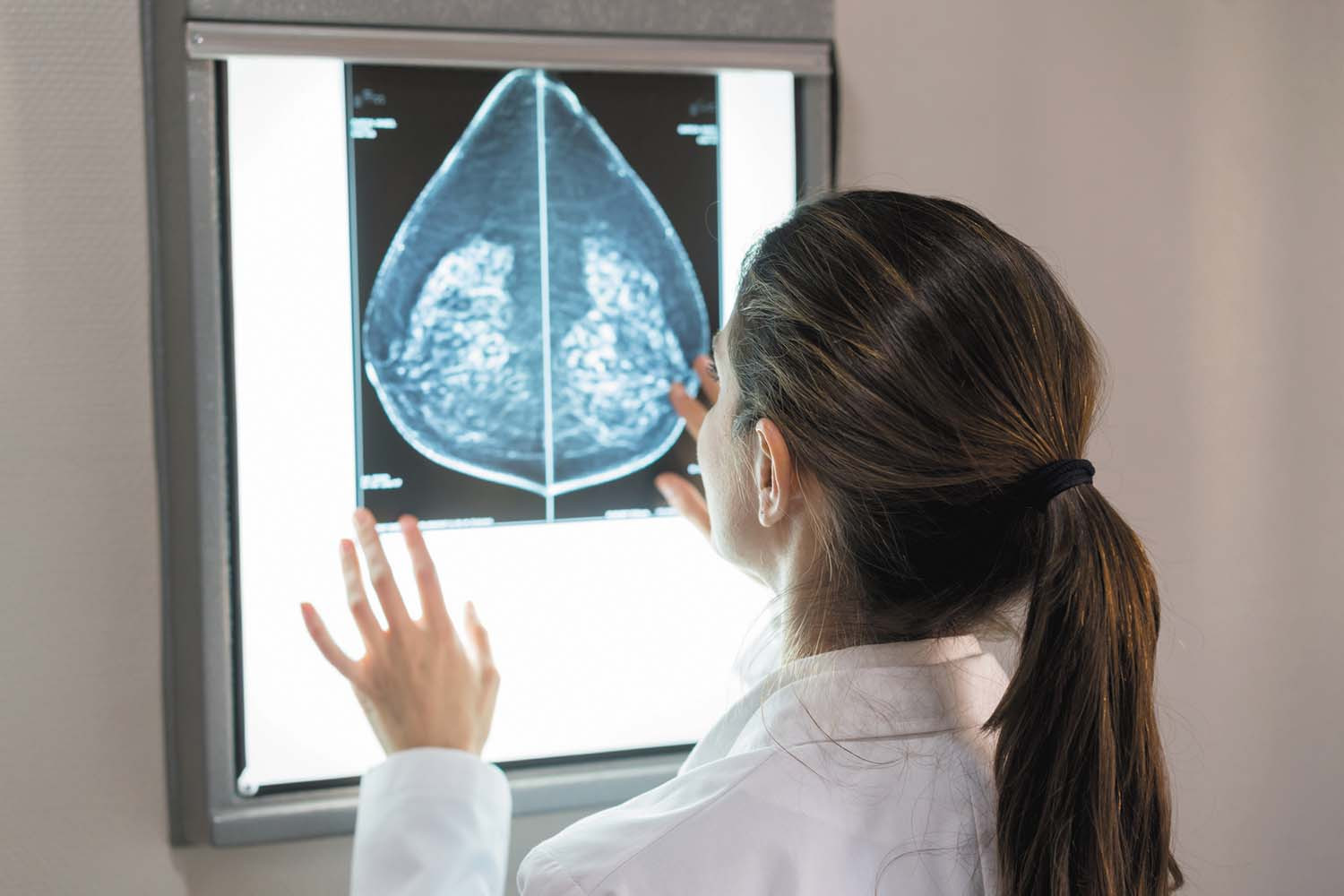
Researchers test new technology for screening dense breasts
Research we're watching
Can a new breast screening technology find more cancers in women with dense breast tissue? A study managed by the American College of Radiology (ACR) Center for Research and Innovation will compare contrast-enhanced spectral mammography (CESM) to other screening technologies used for dense breasts (those that contain a higher proportion of active tissue than fat). It's difficult to find cancers in dense breast tissue using traditional mammography because the active tissue shows up as white areas on a mammogram, just like cancers do, making abnormalities harder to see.
CESM is similar in some ways to traditional mammography, but before having the usual x-ray, the woman is injected with a special iodine-based contrast agent that highlights abnormal areas on the image more clearly. Cancerous tumors typically create new blood vessels when they form, and the contrast agent can reveal that increased blood flow, alerting the radiologist to a potential cancer.
Could your breast implants be making you sick?
Many women are reporting symptoms they believe are associated with their breast implants. Sometimes called breast implant illness, this combination of vague symptoms—such as hair loss, fatigue, anxiety, and depression—is also associated with a number of other conditions, including menopause, thyroid problems, and autoimmune conditions. Researchers are now working with patient advocacy groups to better understand the problem. Experts recommend that women understand the potential risks and benefits of breast implants before having the surgical procedure.
Gene tests for all women with breast cancer could save money — and lives
Research we're watching
Doing genetic tests on all women with breast cancer, as compared with the typical practice of just testing those with a family history of the disease, is worth the extra cost, according to a study published online Oct. 3, 2019, by JAMA Oncology. The study authors say their findings should prompt the expansion of genetic testing to all women diagnosed with breast cancer. It's clear that testing breast cancer patients for genetic variants that raise breast cancer risk (such as BRCA1, BRCA2, and PALB2) would enable doctors to identify more women who carry these variants and who might benefit from preventive strategies. But researchers wondered whether doing so would be too costly. To answer that question, they used a computer model to analyze data from more than 11,000 women. They found that not only would the cost of testing all American women with breast cancer be balanced out by later savings on health care services, but also that just one year of testing could prevent an estimated 9,700 new cases of breast and ovarian cancer and 2,400 deaths.
Image: voinSveta/Getty Images
Hormones and breast cancer: What you should know
New research again links increased breast cancer risk to longer use of hormone therapy.
The link between hormone therapy and breast cancer has been recognized for years. But an analysis published Aug. 29, 2019, in The Lancet has added some additional information to the discussion. The analysis looked at 58 studies that included information on the type and timing of hormone use in individual women, and their body mass index. Researchers began gathering the studies in 1992 and continued until 2018.
We asked Dr. Wendy Chen, an assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, to help us sort through both the old and new information on hormone use and breast cancer and what it means for women considering starting hormone therapy.
High risk for breast cancer? You might benefit from preventive medication
Research we're watching
Women at high risk for breast cancer might benefit from taking medication to prevent the disease, says a new recommendation from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF), a national group of experts. Medications such as tamoxifen (Nolvadex), raloxifene (Evista), and aromatase inhibitors have been shown to help prevent invasive, estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer, but they can cause serious side effects, such as other cancers and blood clots. For some women, the potential benefits of these drugs outweigh those risks. The USPSTF, however, recommends against routine use of these medications for women who are not at high risk for breast cancer, because the potential benefit is much smaller. Women who are over age 35 and are at high risk for breast cancer or who have had previous benign breast lesions (such as atypical ductal or lobular hyperplasia or lobular carcinoma in situ) might want to discuss this recommendation with their doctor. The USPSTF encouraged doctors to weigh the risk of breast cancer against potential drawbacks of the medications and the individual woman's risk for adverse effects.
Image: ShutterOK/Getty Images

Driving with arthritis pain: Stay comfortable — and safe — behind the wheel

Daily cup of coffee may prevent afib recurrence

Gene-editing therapy lowers harmful blood fats in early study

What is EMDR therapy, and who can it help?

GLP-1 drugs versus bariatric surgery for treating obesity

Two dumbbells, three exercises, and 10 minutes

Easing the emotional burden of IBS

Modify your push-ups to meet your fitness level

What is long QT syndrome?

Stroke survivors may benefit from very low LDL levels
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up