Aldosterone overload: An underappreciated contributor to high blood pressure

Can you retrain your brain to stop excessive drinking?

Beyond statins: New ways to lower LDL cholesterol

What is a cardioversion procedure?

Waking up to urinate at night affects blood pressure

Reversing prediabetes may slash heart disease risk by half

For now, electric cars appear safe for people with implanted heart devices

Finding and fixing a stiff, narrowed aortic valve

Can you stop blood thinners after an ablation for atrial fibrillation?

VO2 max: What it is and how you can improve it
Women's Health Archive
Articles
What do vaginal probiotics do?
Vaginal probiotics contain live microorganisms and come in oral and suppository forms. Some ads claim these products can prevent or treat infections. But the vagina regulates its own bacterial mix, so vaginal probiotics aren't necessary.
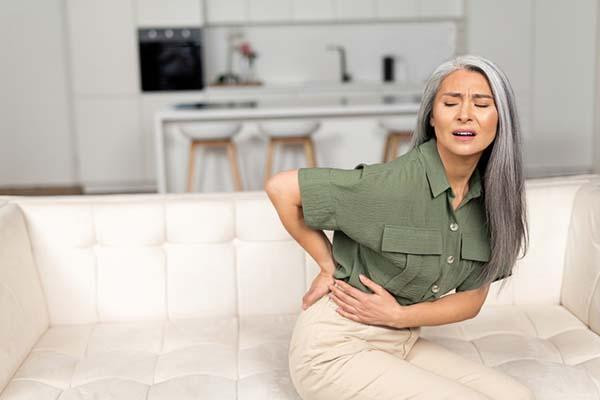
The overlap between back pain and pelvic floor dysfunction
Pelvic floor dysfunction in women is commonly linked to lower back pain. The odds of developing pelvic floor-related back pain increase for women as they get older due to factors such as diminished estrogen and childbirth-related pelvic floor damage. Lower back pain and pelvic floor dysfunction may also have overlapping signs, including urinary leakage or urgency, a feeling of heaviness in the pelvis or vaginal bulging, constipation or bowel issues, painful sex or urination, and pain with prolonged sitting or standing.
The 3 a.m. wake-up: Why it happens to women more often after 55
Waking up in the middle of the night happens to women more often after age 55 due to many factors. These include diminished hormones and circadian rhythm changes. Stress, bladder changes, medications, chronic pain, and alcohol and caffeine use can also contribute. People can break the cycle of nighttime wake-ups by practicing good sleep hygiene, addressing medical issues, trying mind-body techniques such as deep breathing or meditation, and limiting caffeine, alcohol, and heavy evening meals.
What raises your risk for gynecologic cancer?
Gynecologic cancers, which affect the ovaries, uterus, cervix, vagina, or vulva, are less common than breast cancer. Women can guard against these cancers by learning the risk factors for each type, which include obesity, exposure to human papillomavirus, and smoking. Women should also continue pelvic exams and cervical cancer screenings after a hysterectomy or menopause, as well as watch for unusual symptoms. Women with a strong family history of gynecologic or certain other cancers should consider genetic testing.
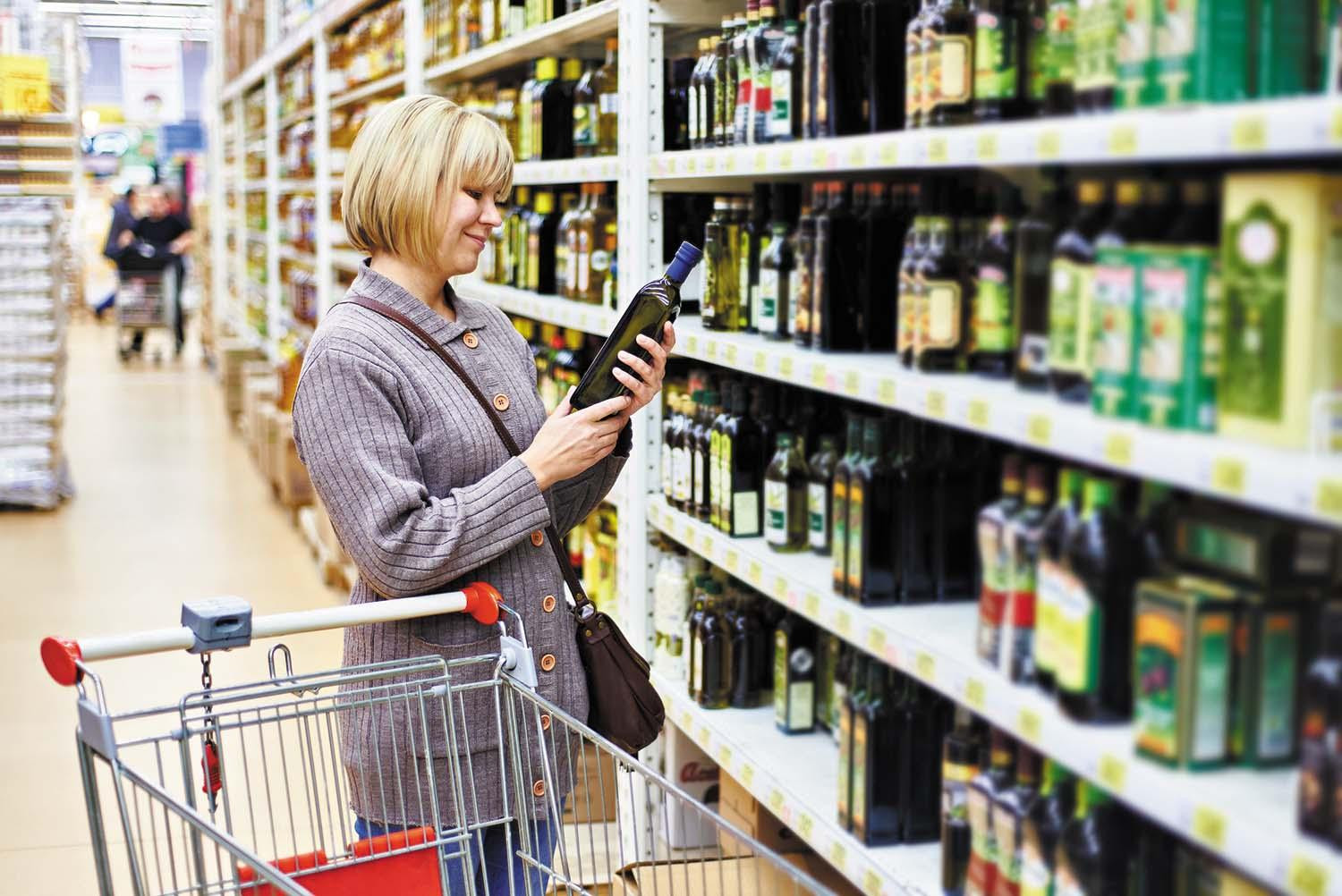
Olive oil may reduce breast cancer risk
A 2025 study suggests that consuming more olive oil may lower women's risk of developing breast cancer, especially certain more aggressive types.
Is acetaminophen safe during pregnancy?
A statement from a group of doctors and scientists raised concerns around taking acetaminophen during pregnancy, but research backing this is based on observational studies and animal studies, so that no firm conclusions can be drawn from it. Here's what to consider if you're pregnant.
Decoding your breast cancer risk
Breast cancer risk assessment scores can enable clinicians to estimate a woman's risk of developing invasive breast cancer over the next five years, as well as her lifetime risk. The tools ask users about myriad factors that influence breast cancer risk. But risk calculators don't necessarily provide the kind of precision and insight some women seek. A risk score can't tell a woman for certain whether she will or won't develop breast cancer. Risk calculators typically also don't determine when or how often most women should seek mammograms.
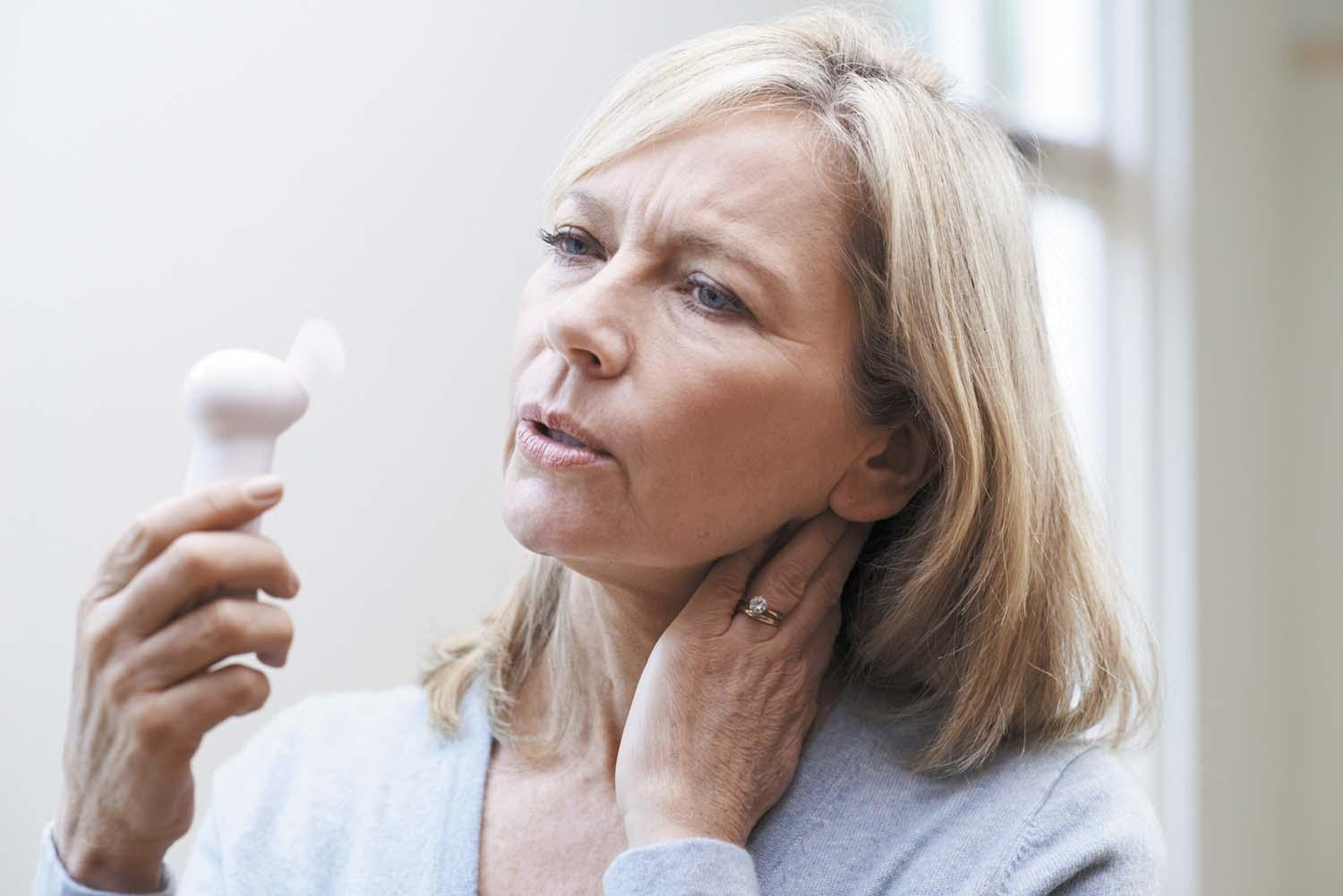
Are hot flashes a warning sign?
Menopausal hot flashes and night sweats, called vasomotor symptoms, are linked in research to higher odds of dementia and cardiovascular disease. But studies don't necessarily account for other health and lifestyle factors that influence brain and heart health. Women who are physically active and have a lower body mass index are less likely to become cognitively impaired. Disrupted sleep, which is common for women with vasomotor symptoms, may also contribute to cardiovascular and cognitive problems.
Does hormone therapy delay menopause?
Using hormone therapy, which involves taking estrogen and sometimes progesterone, doesn't stop or slow the approach of menopause. The arrival of menopause is determined by women's ovaries, not by the amount of these hormones in the body.

Aldosterone overload: An underappreciated contributor to high blood pressure

Can you retrain your brain to stop excessive drinking?

Beyond statins: New ways to lower LDL cholesterol

What is a cardioversion procedure?

Waking up to urinate at night affects blood pressure

Reversing prediabetes may slash heart disease risk by half

For now, electric cars appear safe for people with implanted heart devices

Finding and fixing a stiff, narrowed aortic valve

Can you stop blood thinners after an ablation for atrial fibrillation?

VO2 max: What it is and how you can improve it
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up