Driving with arthritis pain: Stay comfortable — and safe — behind the wheel

Daily cup of coffee may prevent afib recurrence

Gene-editing therapy lowers harmful blood fats in early study

What is EMDR therapy, and who can it help?

GLP-1 drugs versus bariatric surgery for treating obesity

Two dumbbells, three exercises, and 10 minutes

Easing the emotional burden of IBS

Modify your push-ups to meet your fitness level

What is long QT syndrome?

Stroke survivors may benefit from very low LDL levels
Digestive Health Archive
Articles
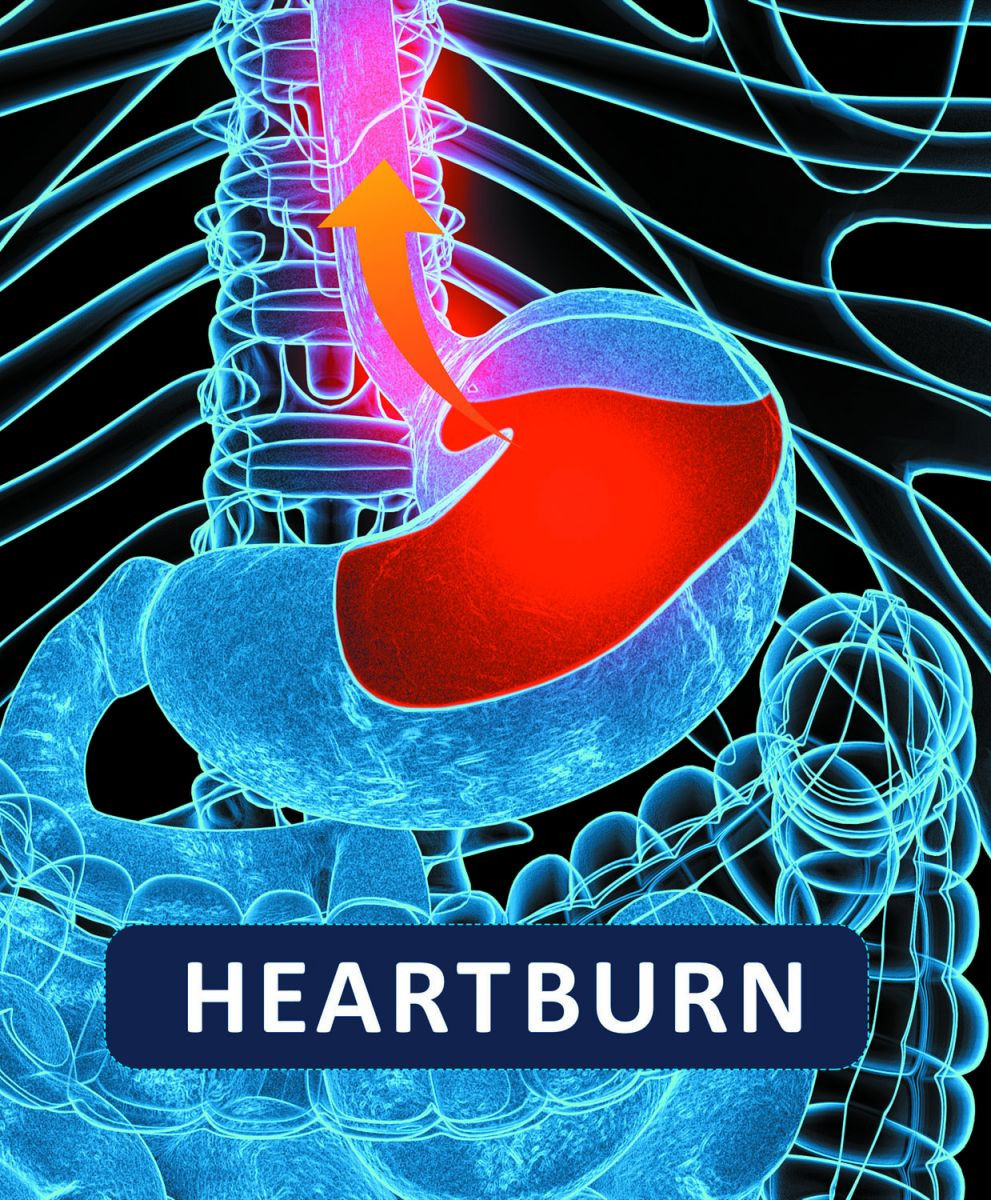
Digestive enzyme supplements for heartburn?
A digestive enzyme supplement can be helpful for people who have difficulty digesting certain foods, but taking one to treat a condition such as heartburn may or may not provide any relief.
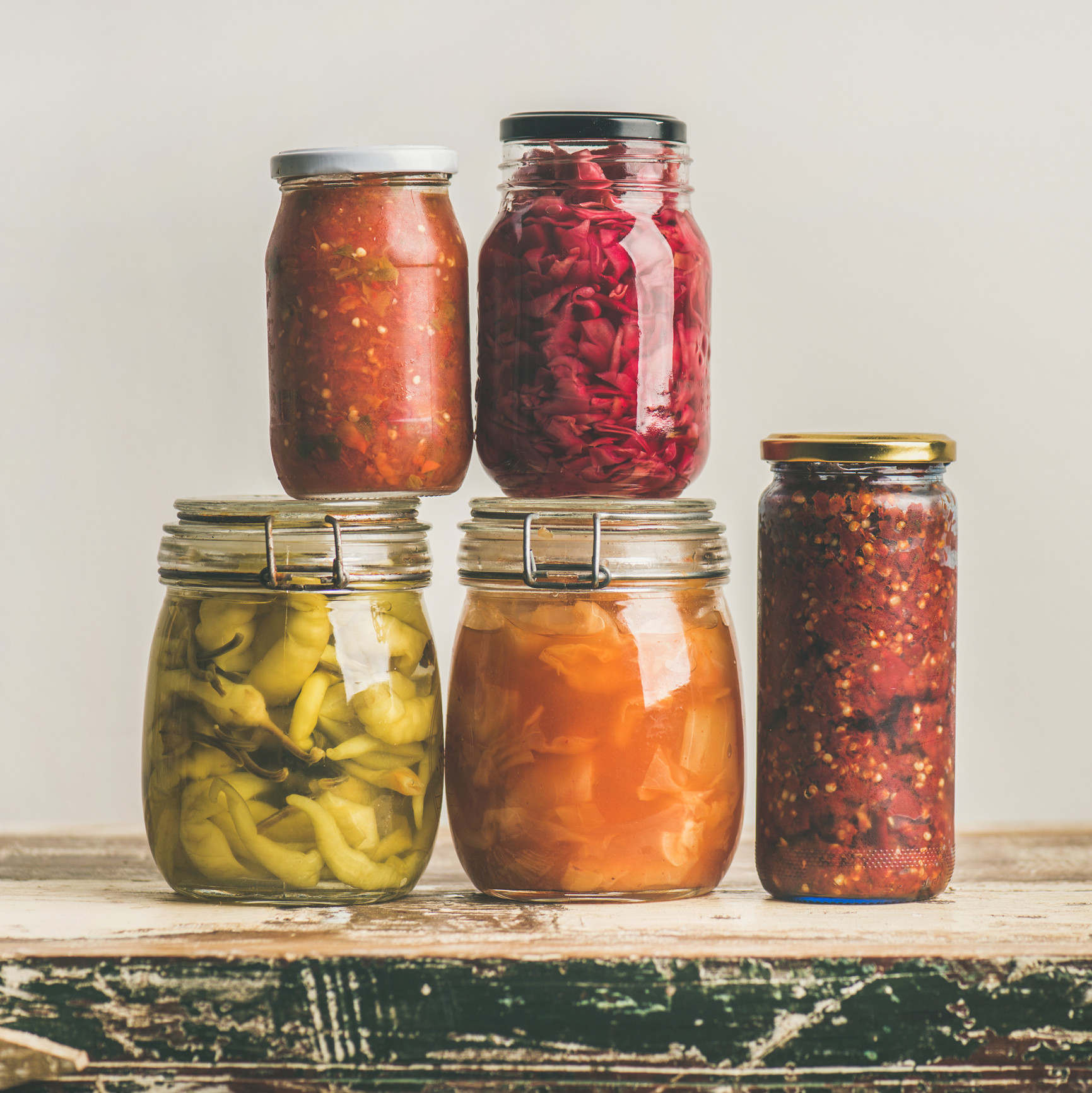
Fermented foods for better gut health
Naturally fermented foods have been getting the attention of health experts because they contain beneficial probiotics that may help strengthen your gut biome — the bacteria and microorganisms in your digestive tract.

Driving with arthritis pain: Stay comfortable — and safe — behind the wheel

Daily cup of coffee may prevent afib recurrence

Gene-editing therapy lowers harmful blood fats in early study

What is EMDR therapy, and who can it help?

GLP-1 drugs versus bariatric surgery for treating obesity

Two dumbbells, three exercises, and 10 minutes

Easing the emotional burden of IBS

Modify your push-ups to meet your fitness level

What is long QT syndrome?

Stroke survivors may benefit from very low LDL levels
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up