Aldosterone overload: An underappreciated contributor to high blood pressure

Can you retrain your brain to stop excessive drinking?

Beyond statins: New ways to lower LDL cholesterol

What is a cardioversion procedure?

For now, electric cars appear safe for people with implanted heart devices

Can you stop blood thinners after an ablation for atrial fibrillation?

Reversing prediabetes may slash heart disease risk by half

Waking up to urinate at night affects blood pressure

Finding and fixing a stiff, narrowed aortic valve

VO2 max: What it is and how you can improve it
Women's Health Archive
Articles
Telltale signs of vaginal infections
Vaginal infections are highly common and often involve symptoms such as vaginal itching, burning, irritation, discharge, and odor. The most prevalent vaginal infections include bacterial vaginosis, yeast infection, trichomoniasis, herpes simplex virus 2, gonorrhea, and chlamydia.
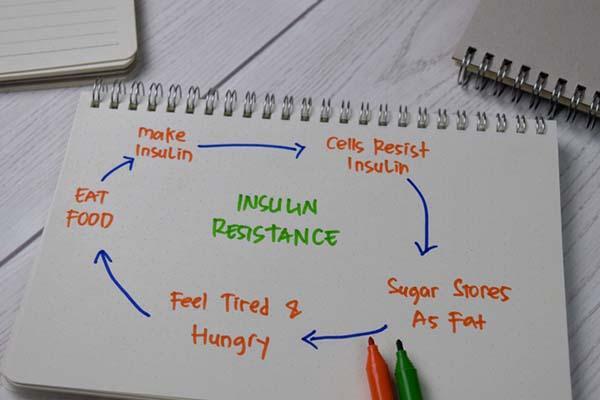
Insulin resistance in women and why it rises after 50
Insulin resistance is when the pancreas makes insulin but the body's cells don't use it efficiently. It becomes more common in women after age 50 due to hormonal shifts that change the way the body stores fat. It is a key step in the process of developing prediabetes and diabetes.
What can I expect during an endometrial biopsy?
An endometrial biopsy is the only way to rule out endometrial (or uterine) cancer. Any vaginal bleeding a year or more after a woman's final period raises the possibility of uterine cancer. The biopsy involves using a suction tube to gather cells from the uterine lining.
What do vaginal probiotics do?
Vaginal probiotics contain live microorganisms and come in oral and suppository forms. Some ads claim these products can prevent or treat infections. But the vagina regulates its own bacterial mix, so vaginal probiotics aren't necessary.
Heart failure symptoms in women: How they're different
After menopause, women develop heart failure at rates similar to men. But women tend to develop heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, which leads to more frequent hospitalizations. Women also have different risk factors for heart failure than men.
Strong is the new skinny
Fitness ideals for women have evolved to prioritize a strong body rather than a slim figure. Strength training counteracts age-related muscle loss and offers a wide variety of additional health benefits. Cardio boosts heart health, but can't substitute for strength training.
Risk-based breast screenings as effective as annual mammograms
A 2025 study suggests that adjusting the intensity of breast cancer screening based on individual risk factors is as effective as annual mammograms.

Aldosterone overload: An underappreciated contributor to high blood pressure

Can you retrain your brain to stop excessive drinking?

Beyond statins: New ways to lower LDL cholesterol

What is a cardioversion procedure?

For now, electric cars appear safe for people with implanted heart devices

Can you stop blood thinners after an ablation for atrial fibrillation?

Reversing prediabetes may slash heart disease risk by half

Waking up to urinate at night affects blood pressure

Finding and fixing a stiff, narrowed aortic valve

VO2 max: What it is and how you can improve it
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up