Driving with arthritis pain: Stay comfortable — and safe — behind the wheel

Daily cup of coffee may prevent afib recurrence

Gene-editing therapy lowers harmful blood fats in early study

What is EMDR therapy, and who can it help?

GLP-1 drugs versus bariatric surgery for treating obesity

Two dumbbells, three exercises, and 10 minutes

Easing the emotional burden of IBS

Modify your push-ups to meet your fitness level

What is long QT syndrome?

Stroke survivors may benefit from very low LDL levels
Mental Health Archive
Articles
Safe injection sites and reducing the stigma of addiction
The scope of the opioid crisis in the US has led some communities to revise their view of substance use disorders. One idea is creating supervised injection facilities that would provide a safe environment and make treatment resources available.
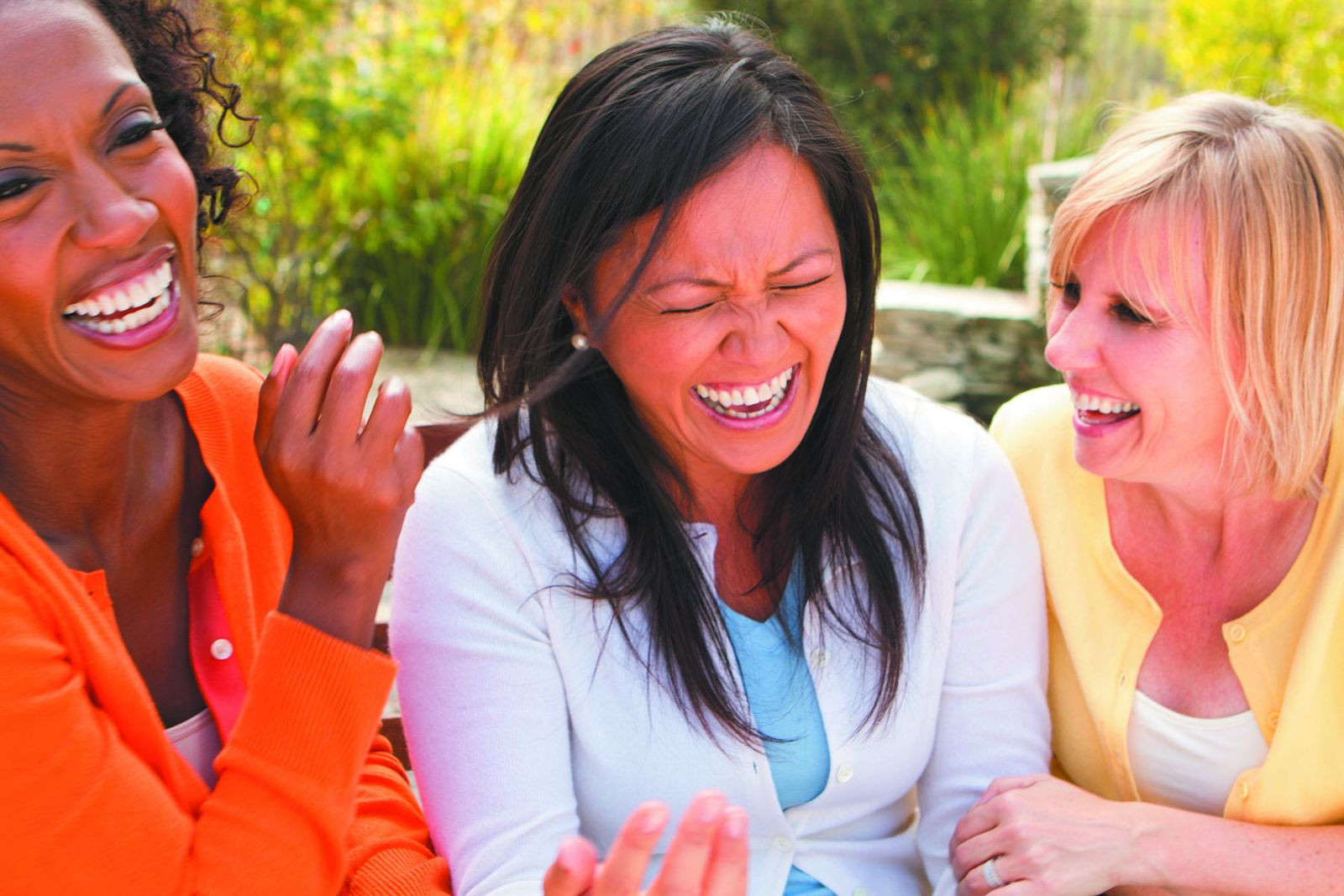
Can relationships boost longevity and well-being?
Harvard research suggests meaningful relationships are a prescription for better emotional, mental, and physical health.
Image: © digitalskillet/Thinkstock
You probably know there are many ways to improve your well-being and chances of living longer, such as exercising more or eating better. But did you know that maintaining meaningful relationships also may play an important role in health, happiness, and longevity? "Good, close relationships appear to buffer us from the problems of getting old," says Dr. Robert Waldinger, a psychiatrist with Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts General Hospital.
Eight decades of research
Dr. Waldinger is the current director of the Harvard Study of Adult Development, an ongoing analysis that's followed more than 700 men since they were teenagers in 1938. More than 60 of the original participants, now in their 90s, are still taking part.
Looking for early signs of Alzheimer’s
By the time memory loss shows up, the disease is well under way. Researchers are finding ways that may reveal brain changes sooner.
For a long time, memory loss was seen as the telltale sign of Alzheimer's disease. While this is certainly the most common symptom, it may not be the best way to identify the disease in its early stages.
"A major problem of Alzheimer's diagnosis, and ultimately effective treatment, is that by the time the first clinical symptoms appear, irreversible damage to the brain has already occurred," says Dr. Seth Gale, a neurologist with Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women's Hospital. "It is now believed that Alzheimer's-related changes begin in the brain at least a decade before any symptoms emerge."
What does it take to be a super-ager?
Research suggests that moving out of your comfort zone is the key to staying mentally and physically young.
Finding role models who are older than we are gets more difficult as we age. But in the last few years, medical science has identified a new group we can aspire to join — the super-agers. The term refers to people in their 70s and 80s who have the mental or physical capability of their decades-younger counterparts.
What makes a cognitive super-ager?
Dr. Bradford Dickerson, a neurologist at Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts General Hospital and his colleagues have been studying super-agers for several years. Their results suggest that embracing new mental challenges may be the key to preserving both brain tissue and brain function.
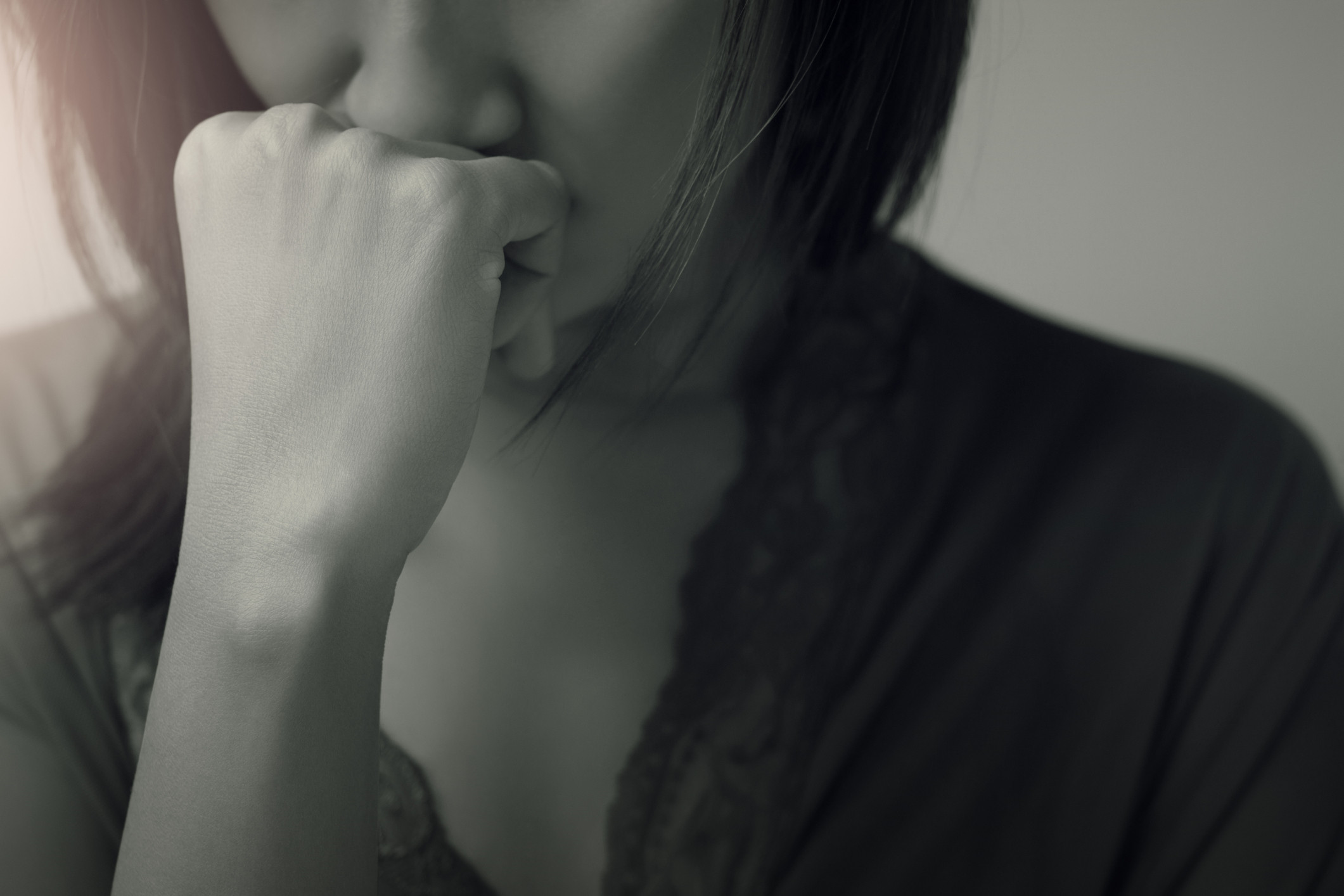
How depression affects your thinking skills
Don't assume age is to blame for changes in memory, attention, and decision making.
Image: © pixelheadphoto/Thinkstock
Depression has a way of sucking the joy and meaning from life. Chronic feelings of hopelessness, apathy, or despair are part of the condition. It may also bring physical symptoms, such as weight loss, sleep disturbance, fatigue, and aches and pains. But depression can be sneaky, causing subtle changes in thinking skills that you may not attribute to the condition. "Very often, one of the first signs of depression in people ages 70 or older is a change in thinking," says Dr. Helen Farrell, a psychiatrist with Harvard-affiliated Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
What's the connection?
Depression may involve the interruption or reduction of chemical messengers in the brain called neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. These chemical changes may be the cause of your depression (if the brain systems that regulate them go awry), or they may result from other depression triggers, such as the following:
Physicians and opioids: Part of the solution, but challenges ahead
As doctors acknowledge the role that they have played in the current opioid crisis, they, along with hospitals, medical schools, and other members of the medical community have worked to address the issue on several fronts, including instituting prescribing guidelines and offering continuing education to prescribers.

Driving with arthritis pain: Stay comfortable — and safe — behind the wheel

Daily cup of coffee may prevent afib recurrence

Gene-editing therapy lowers harmful blood fats in early study

What is EMDR therapy, and who can it help?

GLP-1 drugs versus bariatric surgery for treating obesity

Two dumbbells, three exercises, and 10 minutes

Easing the emotional burden of IBS

Modify your push-ups to meet your fitness level

What is long QT syndrome?

Stroke survivors may benefit from very low LDL levels
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up