New thinking about plaque in arteries that feed the brain

Want to prevent shifting teeth? Maybe you need retainers

New evidence that polyphenol-rich foods help the heart

What you need to know about the new dietary guidelines

Food that’s healthier for people and planet can be cheaper, too

What are somatic workouts?

How to curb your stress eating

8 simple ways to reduce ultra-processed foods in your diet

How to spot Parkinson’s disease symptoms

Heart failure symptoms in women: How they’re different
Men's Health Archive
Articles
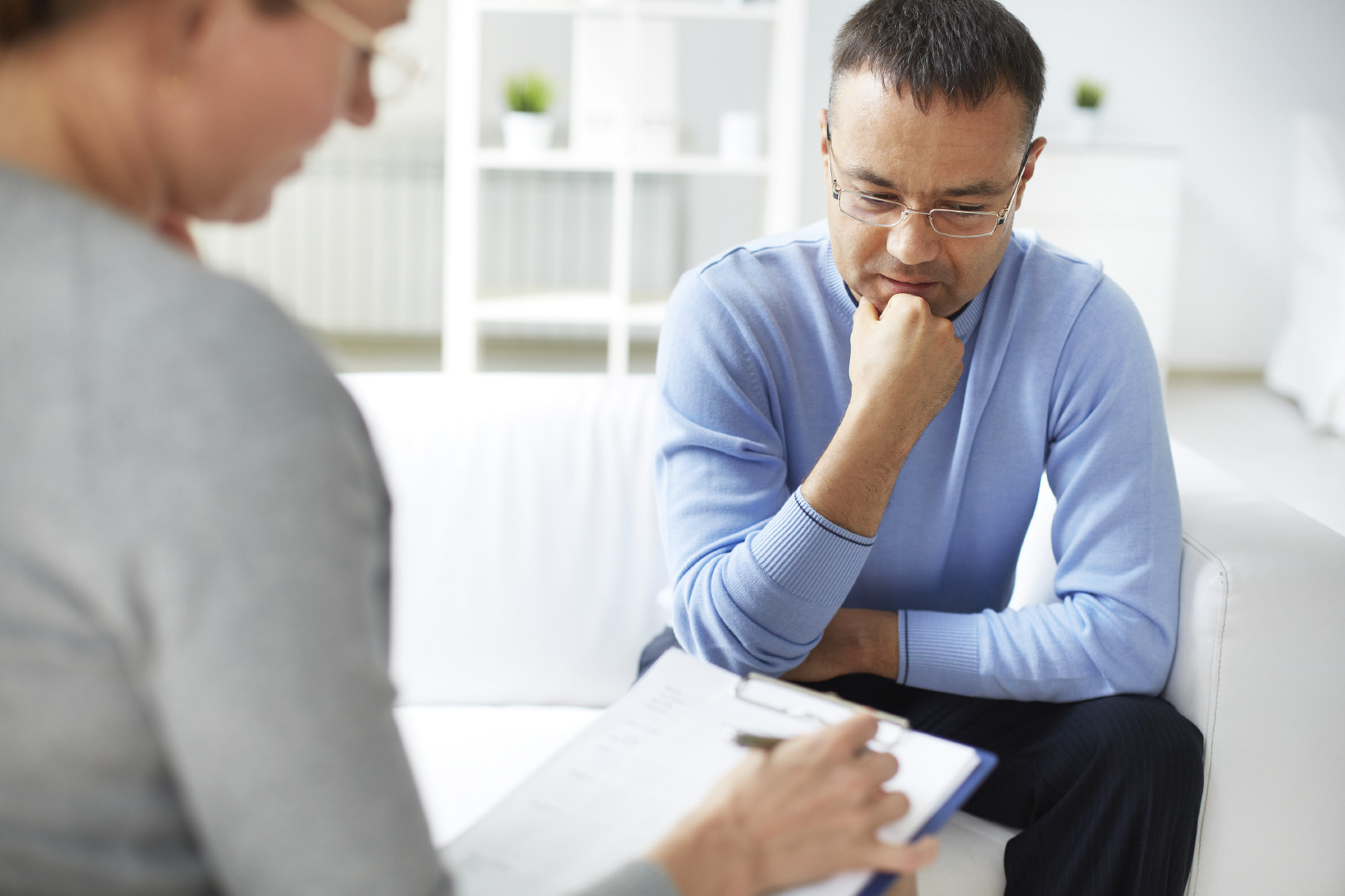
What a therapist can do for you
Many men resist talking about their problems, but there are times when it's necessary.
Image: ArtemSam/Thinkstock
Men often like to think of themselves as the strong, problem-solver type who never needs help, especially when it comes to their emotional and mental issues. But men should never bottle up their feelings and tough it out, according to Dr. Darshan Mehta, medical director of the Benson-Henry Institute for Mind Body Medicine at Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts General Hospital.
"Your mental health is equally as important as your physical health and proper nutrition. Not addressing negative feelings can carry over to all aspects of your life and have a profound impact," he says.
Can vitamin D levels signal aggressive prostate cancer?
Low levels of vitamin D may help predict aggressive prostate cancer, according to new research. While it only showed an association, the researchers believe low D levels could be used as a valuable biomarker, and help men and their doctors decide whether to consider active surveillance, in which the cancer is monitored for changes.
Prompt attention to “ministrokes” may reduce risk of subsequent stroke
Getting immediate attention for symptoms of a transient ischemic attack can minimize the risk of a subsequent stroke.
The risks of active surveillance for men with intermediate-risk prostate cancers
Many men with prostate cancer benefit from active surveillance, in which treatment doesn’t begin unless the cancer spreads. There has been some debate about whether this strategy is safe for men with intermediate-risk prostate cancer. A new study suggests that this type of cancer is more likely to spread than previously thought — but active surveillance can still be a good option for many intermediate-risk men.
What men can gain from therapy
Men are often reluctant to seek therapy. After all, it involves asking for help and talking candidly about one’s emotions, two things that many men are eager to avoid. But men should know that there’s no need to “tough out” whatever they’re going through. There are plenty of professionals out there who are ready and willing to lend an ear.
A new look at testosterone therapy
Declining testosterone is a normal part of aging, but is replacement therapy right for you? Here is what you need to know.
Image: aquarius83men/Thinkstock
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) has surged in popularity over the past decade. Millions of older men have turned to TRT to restore hormone levels in hopes of refueling energy and reigniting their sex drive.
Yet TRT remains controversial because of its uncertain benefits and potential health risks. Safety concerns were raised years ago when studies showed a possible association between TRT and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
Should you take “senior” multivitamins?
There is little scientific proof that multivitamins or special “senior” vitamin formulas helps you live longer, feel better, or avoid disease. Spending money on fresh fruits and vegetables is a wiser and healthier investment.
Concern about recurring hiccups
Hiccups are often caused by many everyday situations, including distention of the stomach (which can be the result of overeating), swallowing air, or drinking carbonated beverages. They usually go away on their own, but episodes that last longer than 48 hours could be a sign of certain medical problems.
Sunscreen confusion
Men may not be doing all they need to protect themselves from sun damage and skin cancer.
Image: JupiterImages/Thinkstock
Proper protection against skin cancer continues to be relevant once a man hits age 65. "Unfortunately, ultraviolet [UV] exposure and damage is cumulative over our lifetimes," says Dr. Joseph Merola, a dermatologist with Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women's Hospital. "There is no safe age at which we can put down the sunscreen or stop thinking about sun protection."
Even if men are aware of the dangers of sun exposure, new research shows most do not follow basic guidelines. A study published June 17, 2015, in JAMA Dermatology found that only 14.3% of men surveyed reported they regularly use sunscreen. The study also found that men were more likely than women to never use sunscreen—43.8% of men compared with 27% of women—and perhaps most telling, only 7% knew what to look for on a sunscreen label.
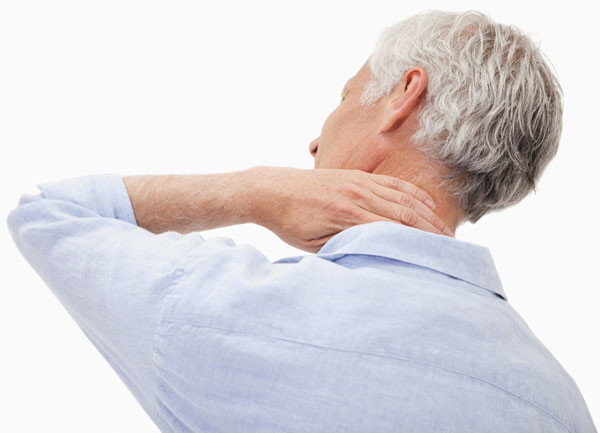
Turn away from neck pain
Poor lifestyle habits can trigger chronic neck pain that impedes daily activities and raises your risk of serious health issues.
Muscle strains caused by poor posture and sleeping positions often trigger neck pain.
Image: wavebreakmedia/Thinkstock
Neck pain is a nagging ailment that affects everyone at some time. In fact, approximately 80% of people experience neck pain during their lifetime, and 20% to 50% deal with it annually, according to Dr. Frank Pedlow, an orthopedic spine surgeon at Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts General Hospital.

New thinking about plaque in arteries that feed the brain

Want to prevent shifting teeth? Maybe you need retainers

New evidence that polyphenol-rich foods help the heart

What you need to know about the new dietary guidelines

Food that’s healthier for people and planet can be cheaper, too

What are somatic workouts?

How to curb your stress eating

8 simple ways to reduce ultra-processed foods in your diet

How to spot Parkinson’s disease symptoms

Heart failure symptoms in women: How they’re different
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up