What are somatic workouts?

How to curb your stress eating

How to spot Parkinson’s disease symptoms

8 simple ways to reduce ultra-processed foods in your diet

Heart failure symptoms in women: How they’re different

GERD diet: Foods to avoid to reduce acid reflux

Strong is the new skinny

Everyday habits that sneakily weaken your bones

Don’t wait to get help for back pain

Correcting how you walk may ease osteoarthritis knee pain
Mental Health Archive
Articles
Losing a pet can trigger grief as intense as human loss
A 2026 study suggested that losing a pet can trigger grief as intense and prolonged as that from losing a human loved one.
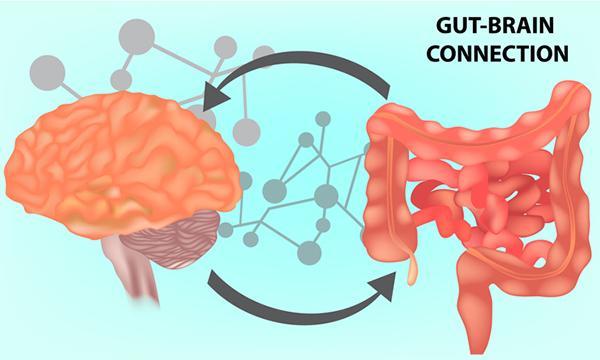
How the gut-brain connection influences mood
The brain communicates with the gastrointestinal tract through a connection scientists call the gut-brain axis. Evidence suggests that when the gut is irritated by triggers such as infection, stress, food, allergies, alcohol, or heredity, the resulting inflammation could influence mood.
What is CBT-i?
Cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-i) identifies and challenges thoughts about sleep that make it more difficult, eradicates bedroom activities other than sleep and sex, limits the time spent in bed to increase the drive to sleep, and teaches relaxation techniques.
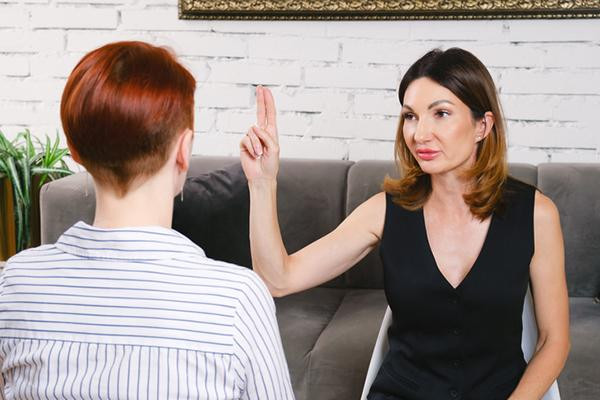
Will couples therapy improve your relationship?
Couples therapy gives partners a structured space to work through conflict, improve communication, and strengthen their bond with the help of a trained therapist. It’s useful not only in times of crisis, but also when couples want to navigate big life changes or simply deepen their connection.
An essential way to combat loneliness
Loneliness is widespread and harms both physical and mental health, but nurturing existing relationships is a powerful antidote. By reconnecting with friends and family, meeting regularly, minimizing distractions, and staying in touch across distance, it’s possible to more connected and help protect long-term health.
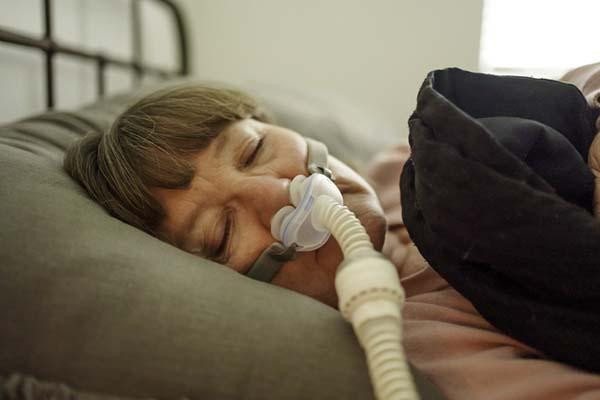
Sleep apnea linked to mental health conditions in middle and older age
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), marked by breathing pauses during sleep, is linked to high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. A 2025 study found that people at high risk for OSA also had about 40% higher odds of depression and other mental health conditions.
What is EMDR therapy, and who can it help?
Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) therapy is recognized as a proven method for treating post-traumatic stress disorder. It also shows promise for other mental health conditions, including personality disorders, anxiety, and depression.
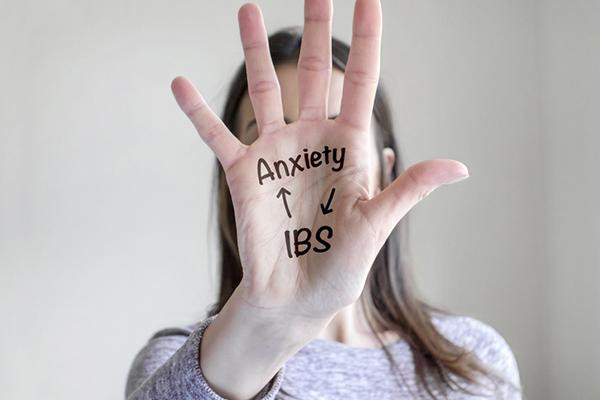
Easing the emotional burden of IBS
People with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) often struggle with stress, anxiety, and depression. Cognitive behavioral therapy and gut-directed hypnotherapy have the strongest evidence for treating these IBS-related issues. Other interventions like aerobic exercise, yoga, acupuncture, and biofeedback also may be helpful.
The emotional aftermath of a heart attack
Up to half of all heart attack survivors experience some type of psychological distress, including sadness, worry, or irritability. This problem is known as post-myocardial infarction psychological distress. Cardiac rehabilitation is the best way to get treatment.
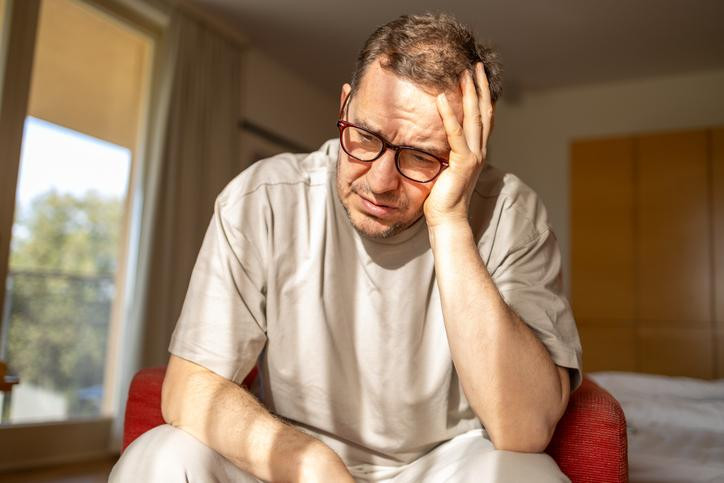
Yes, you can overcome malaise!
Malaise is a feeling of weakness, fatigue, or being generally unwell. Addressing underlying causes and making healthy lifestyle changes — such as exercising regularly, eating a healthy diet, and getting enough sleep — can help people with malaise feel better.

What are somatic workouts?

How to curb your stress eating

How to spot Parkinson’s disease symptoms

8 simple ways to reduce ultra-processed foods in your diet

Heart failure symptoms in women: How they’re different

GERD diet: Foods to avoid to reduce acid reflux

Strong is the new skinny

Everyday habits that sneakily weaken your bones

Don’t wait to get help for back pain

Correcting how you walk may ease osteoarthritis knee pain
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up