How we make memories

Aldosterone overload: An underappreciated contributor to high blood pressure

Can you retrain your brain to stop excessive drinking?

Beyond statins: New ways to lower LDL cholesterol

What is a cardioversion procedure?

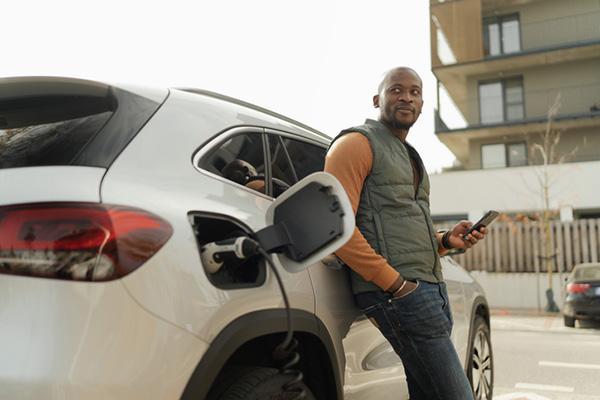
For now, electric cars appear safe for people with implanted heart devices

Can you stop blood thinners after an ablation for atrial fibrillation?

Reversing prediabetes may slash heart disease risk by half

Waking up to urinate at night affects blood pressure

Finding and fixing a stiff, narrowed aortic valve
Heart Health Archive
Articles
For now, electric cars appear safe for people with implanted heart devices
A 2025 review of past research found that electromagnetic field exposure from electric cars poses no immediate health risks for people with implanted heart devices, such as pacemakers or implantable cardioverter-defibrillators.
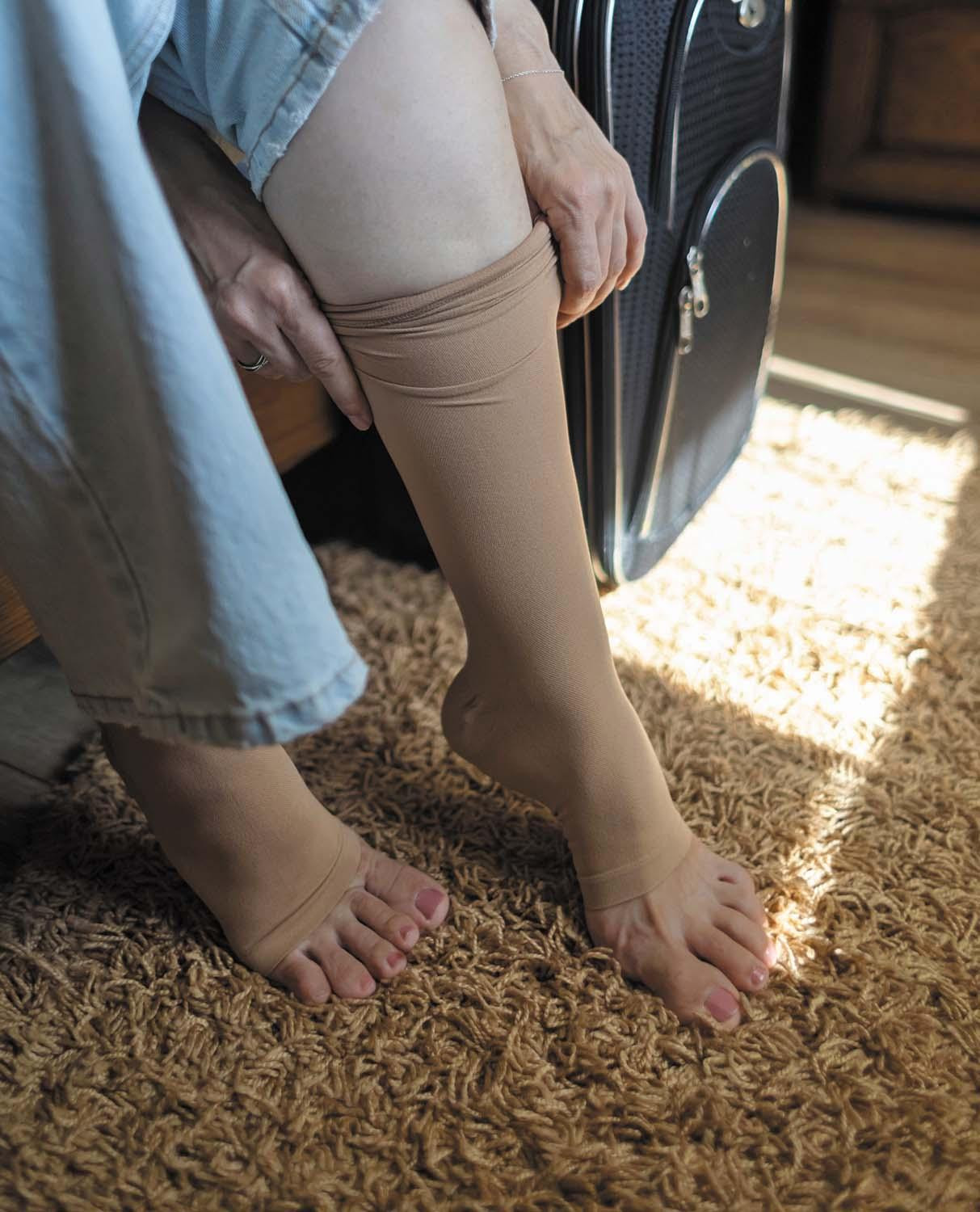
Could you benefit from wearing compression socks?
Compression socks are snug, supportive stockings that can help people who struggle with leg swelling or circulation issues. They're commonly used for certain vein problems or clot risks, and a doctor can help decide who needs them and how to use them.
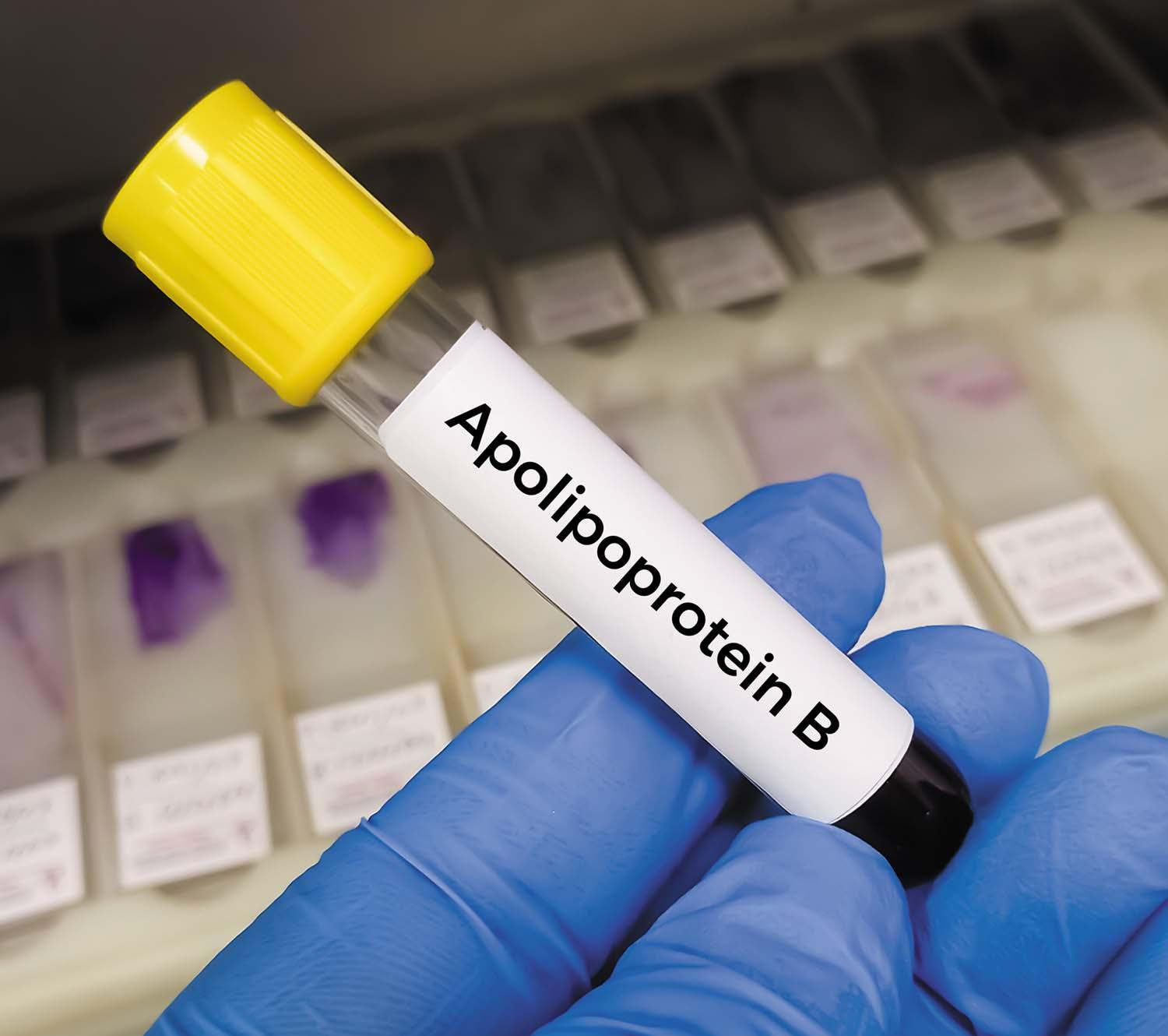
Is an apoB test a better way to check your cholesterol?
ApoB is a protein that attaches to harmful fat particles in the blood to form lipoproteins, including low-density lipoprotein (LDL). An apolipoprotein B (apoB) test counts the number of LDL particles in the bloodstream as well as other particles that can contribute to clogged arteries and heart attacks.
When and why you need drugs for atrial fibrillation
Many people with atrial fibrillation - a rapid, irregular heart rhythm - need medications to control symptoms and lower their risk of stroke. These include drugs that slow down the heart, help restore its rhythm, and prevent blood clots.
Easy ways to fit heart-healthy avocados into your meals
Avocados have a mix of fiber, healthy fat, antioxidants, and key minerals that support heart health. But avocados aren't low-calorie foods. They're best added to the diet by swapping them for something else, such as subbing mashed avocado for butter on toast.
Avoiding triggers for a common cause of fainting
Vasovagal syncope, a common cause of fainting, occurs when the vagus nerve becomes overstimulated in response to triggers such as stress or dehydration. Certain strategies, such as lying down and elevating the legs, help people avoid passing out.
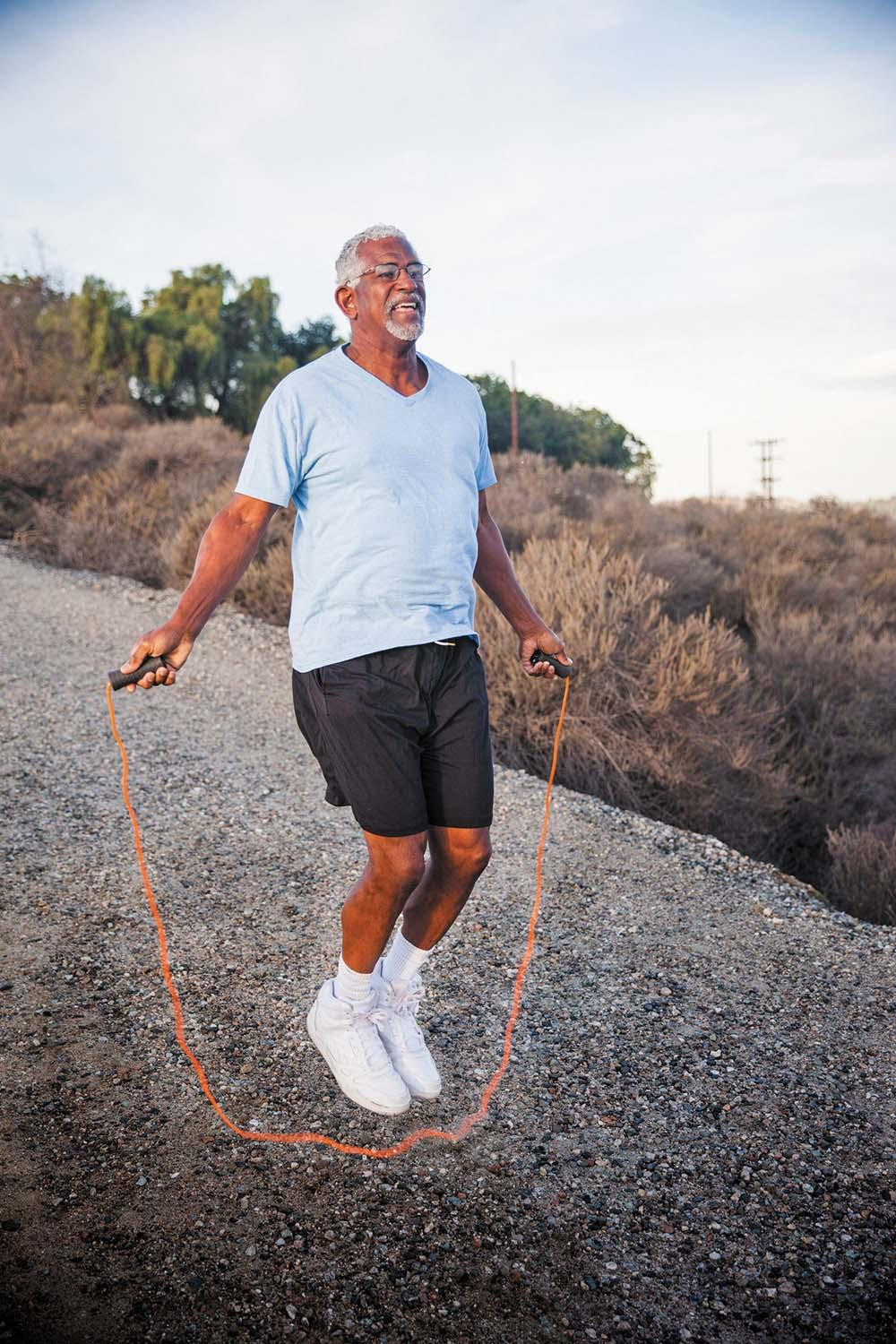
A fresh approach to cardio exercises
There are many ways people can meet the guidelines for weekly activity besides running and walking. They can do activities like boxing, swimming, cycling, basketball, dancing, and pickleball; circuit training using gym machines; and exercising at home.
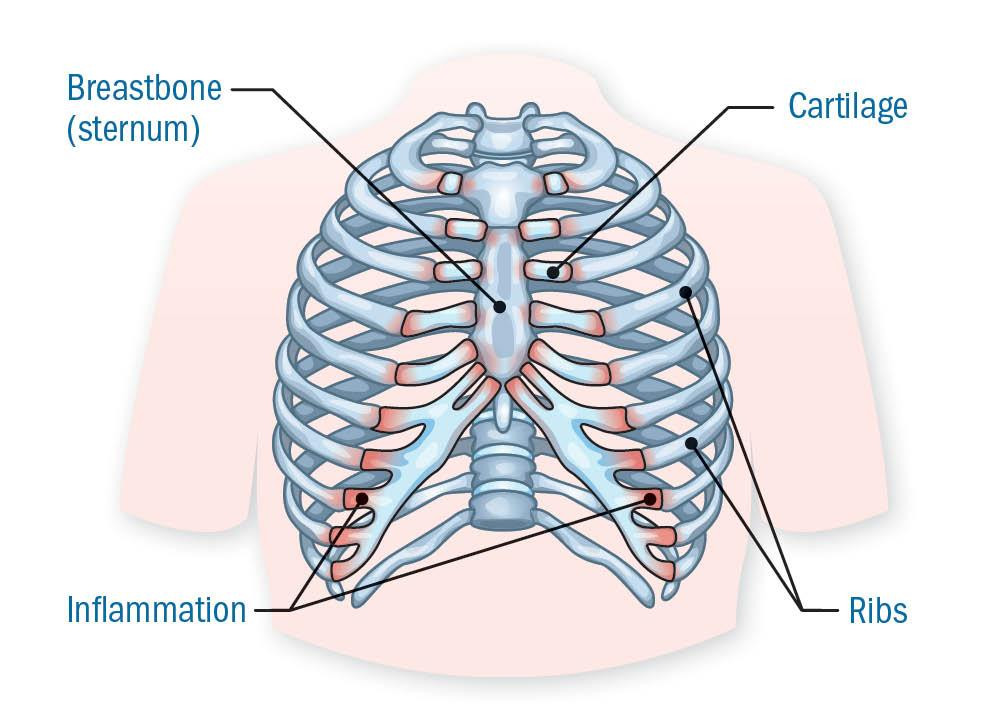
Chest pain that mimics a heart attack
Costochondritis, which is inflammation of the cartilage between the ribs and the breastbone, is one of the most common causes of chest pain and is frequently mistaken for a heart attack.
New thinking about plaque in arteries that feed the brain
Carotid artery stenosis, which happens when fatty plaque accumulates in neck arteries that supply the brain, leaves people vulnerable to a stroke. Intensive drug therapy may forestall the need for invasive procedures to treat this problem.
New evidence that polyphenol-rich foods help the heart
A 2025 study suggests that polyphenols, found in a wide range of plant foods, may have long-term benefits for the heart. Over an average of 11 years, people whose diets contained the most polyphenol-rich foods ranked lowest on scores of heart disease risk.

How we make memories

Aldosterone overload: An underappreciated contributor to high blood pressure

Can you retrain your brain to stop excessive drinking?

Beyond statins: New ways to lower LDL cholesterol

What is a cardioversion procedure?

For now, electric cars appear safe for people with implanted heart devices

Can you stop blood thinners after an ablation for atrial fibrillation?

Reversing prediabetes may slash heart disease risk by half

Waking up to urinate at night affects blood pressure

Finding and fixing a stiff, narrowed aortic valve
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up