What are somatic workouts?

How to curb your stress eating

How to spot Parkinson’s disease symptoms

8 simple ways to reduce ultra-processed foods in your diet

Heart failure symptoms in women: How they’re different

GERD diet: Foods to avoid to reduce acid reflux

Strong is the new skinny

Everyday habits that sneakily weaken your bones

Don’t wait to get help for back pain

Correcting how you walk may ease osteoarthritis knee pain
Heart Health Archive
Articles
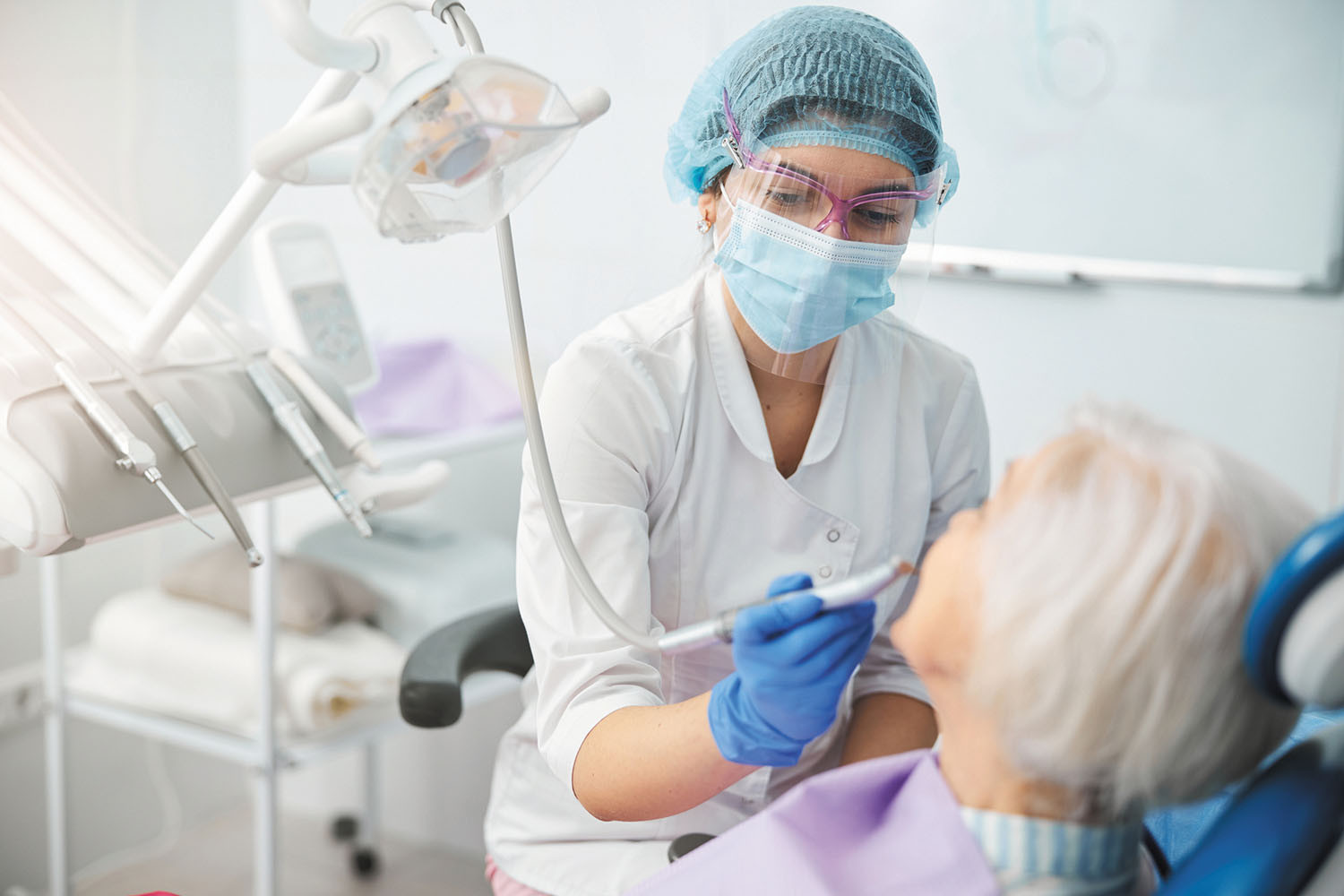
Gum disease and heart health: Probing the link
About two-thirds of people over 65 have periodontal disease, which is linked to a higher risk of heart disease. Shared risk factors such as smoking and an unhealthy diet may explain the association, but bacteria and inflammation could be a common thread. The bacteria responsible for periodontal disease can travel to blood vessels throughout the body and have been found in the fatty debris (atherosclerosis) that clogs arteries located far from the mouth—and in blood clots from people who have experienced heart attacks.
Create a customized home workout space
Having a home workout area can make it easier to meet daily exercise goals, especially during the winter months, when weather conditions may make outdoor exercise impractical. If space allows, people may want a treadmill or other machine that's suitable for any health issues they may have. For example, people with hip or knee arthritis often find that a stationary bike is more comfortable for arthritic joints. For strength training, resistance bands or tubes are ideal for beginners because they're affordable, versatile, and easy to use. Scheduling a few sessions with either a physical therapist or certified personal trainer can help people learn and practice proper form.
Under-the-radar heart risks
Research has shown that men can have a higher risk for heart attacks and strokes if they suffer from certain medical conditions that might seem unrelated to heart disease. These conditions include erectile dysfunction, gum disease, peripheral artery disease, and urinary tract infections. Many factors that contribute to heart disease like inflammation and fatty deposits in the arteries are involved in these other conditions.
An often-silent liver condition that threatens the heart
Many Americans may have a potentially serious condition marked by a buildup of fat inside the liver. Known as metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), it's closely linked to a higher risk of cardiovascular disease. The root of the problem is usually excess weight—especially the accumulation of belly fat known as abdominal obesity. Weight gain can trigger a host of metabolic problems that cause blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels to rise. All of these factors are closely linked to a higher risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Heart disease is one of the common causes of death among people with MASLD.
What you should know about recalls of cardiac devices
Implanted heart devices include pacemakers and implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs), which monitor and correct abnormal heart rhythms. While very reliable, they are not perfect, and recalls of these devices affect thousands of people each year, according to a 2024 study. Testing the effectiveness and safety of cardiac devices is far more complicated than testing drugs. But efforts are under way to improve postmarket tracking of device complications by using electronic health records, Medicare databases, and registries developed in partnership with device manufacturers.
Sleep apnea and heart disease: A weighty matter
Anti-obesity drugs, which can lead to dramatic weight loss, may improve symptoms of sleep apnea. This serious breathing disorder raises the odds of high blood pressure, heart attack, and stroke. Excess weight is the strongest risk factor linked with sleep apnea, which affects about 25% of men and 10% of women in the United States. Extra fat tissue in the neck and throat can narrow the airway, and extra weight on the chest and belly puts pressure on the lungs, which makes the normal process of inhaling and exhaling less effective.
Seafood selections that help your heart — and our planet
Choosing seafood that's lower on the food chain (such as herring, sardines, clams, and oysters) is beneficial for both cardiovascular health and the health of the environment. Finfish, crustaceans, mollusks, cephalopods, aquatic plants, and seaweed are all considered aquatic foods. Replacing terrestrial animal proteins such as beef, pork, and chicken (especially processed forms) with aquatic foods helps people eat less saturated fat and more omega-3 fatty acids. Also, producing aquatic foods generates far fewer greenhouse gases than producing terrestrial foods.
Incorrect arm position may skew blood pressure readings
Letting your arm dangle or rest in your lap (instead of being supported at heart level, as is recommended) during a blood pressure check can cause a falsely high reading, according to a 2024 study.
How are clogged neck arteries treated?
Treatments for severe carotid stenosis include a catheter-based procedure to insert a stent inside the carotid (carotid artery stenting) or surgery to remove the plaque inside the artery (carotid endarterectomy).

What are somatic workouts?

How to curb your stress eating

How to spot Parkinson’s disease symptoms

8 simple ways to reduce ultra-processed foods in your diet

Heart failure symptoms in women: How they’re different

GERD diet: Foods to avoid to reduce acid reflux

Strong is the new skinny

Everyday habits that sneakily weaken your bones

Don’t wait to get help for back pain

Correcting how you walk may ease osteoarthritis knee pain
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up