New thinking about plaque in arteries that feed the brain

Want to prevent shifting teeth? Maybe you need retainers

What you need to know about the new dietary guidelines

Food that’s healthier for people and planet can be cheaper, too

New evidence that polyphenol-rich foods help the heart

8 simple ways to reduce ultra-processed foods in your diet

How to curb your stress eating

How to spot Parkinson’s disease symptoms

Heart failure symptoms in women: How they’re different

GERD diet: Foods to avoid to reduce acid reflux
Diseases & Conditions Archive
Articles
How to get rid of a sinus headache
A sinus headache usually stems from irritated, congested sinuses that create pressure and pain around the eyes, nose, or forehead. Relief often comes from easing inflammation and congestion with a mix of home measures and over-the-counter treatments.
Measles is making a comeback: Can we stop it?
In the US, widespread vaccination halted the ongoing spread of measles more than 20 years ago, but recent outbreaks have flared in over 20 US states, leading to hospitalizations and at least two deaths. Measles is highly preventable — here’s what you need to know.
How to spot Parkinson’s disease symptoms
Parkinson’s disease symptoms tend to develop gradually and can be mistaken for normal aging. Early movement-related signs include tremor in one hand, slower movements, mild balance and gait changes, and muscle stiffness. Other clues include loss of smell, sleep changes, and constipation.
GERD diet: Foods to avoid to reduce acid reflux
Dietary changes can make a big difference for people with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Foods to limit or avoid include chocolate, onions, and tomato sauce. Adjusting eating habits—by eating smaller portions, for example—might also help people avoid heartburn and other symptoms.
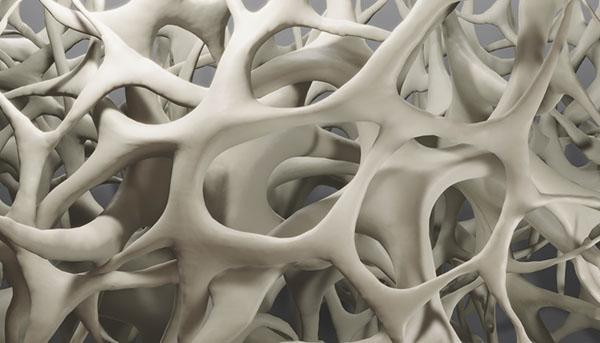
Everyday habits that sneakily weaken your bones
A variety of everyday habits can stealthily reduce bone health. These include consuming too little calcium, excessive caffeine or soda, inadequate protein, and large amounts of alcohol, as well as smoking, being sedentary, dieting frequently, or taking certain medications.
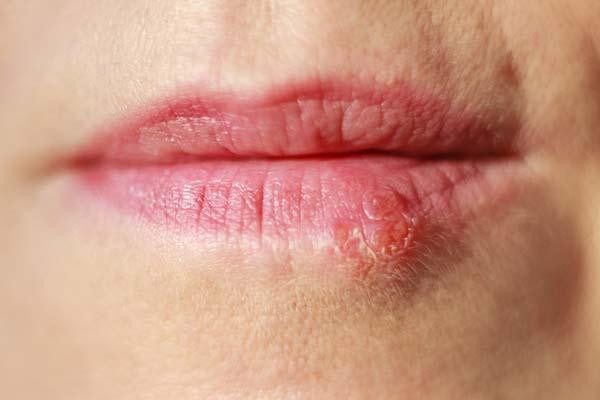
Is there a way to keep cold sores from coming back?
About half of Americans have herpes simplex virus type 1, which causes cold sores that can recur periodically. The virus can’t be eliminated, but topical and oral treatments can help. In addition, people can avoid cold sore triggers such as stress or fatigue.
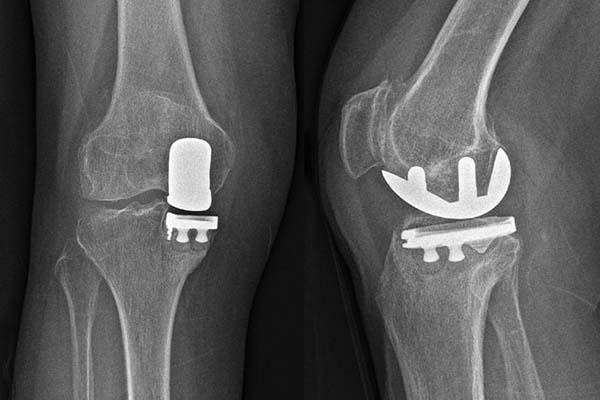
Partial knee replacement as effective as total replacement for select patients
A 2025 study found that for people with advanced knee osteoarthritis in which the damage is limited to one side of the joint, partial knee replacement is as effective as total knee replacement for pain relief and improved function and carries a similar need for additional surgeries within 10 years.
Driving with arthritis pain: Stay comfortable — and safe — behind the wheel
The pain and stiffness of arthritis can make driving difficult, affecting range of motion, grip, and getting in and out of a car. Managing symptoms, using adaptive devices, positioning yourself correctly in the car, and knowing your limits can help you drive comfortably and safely.

New thinking about plaque in arteries that feed the brain

Want to prevent shifting teeth? Maybe you need retainers

What you need to know about the new dietary guidelines

Food that’s healthier for people and planet can be cheaper, too

New evidence that polyphenol-rich foods help the heart

8 simple ways to reduce ultra-processed foods in your diet

How to curb your stress eating

How to spot Parkinson’s disease symptoms

Heart failure symptoms in women: How they’re different

GERD diet: Foods to avoid to reduce acid reflux
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up