Aldosterone overload: An underappreciated contributor to high blood pressure

Can you retrain your brain to stop excessive drinking?

Beyond statins: New ways to lower LDL cholesterol

What is a cardioversion procedure?

Waking up to urinate at night affects blood pressure

Reversing prediabetes may slash heart disease risk by half

For now, electric cars appear safe for people with implanted heart devices

Finding and fixing a stiff, narrowed aortic valve

Can you stop blood thinners after an ablation for atrial fibrillation?

VO2 max: What it is and how you can improve it
Diseases & Conditions Archive
Articles
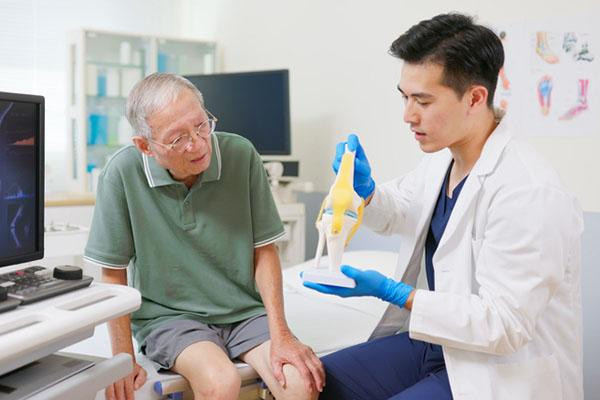
What happens when a joint replacement fails?
Total knee and hip replacements are highly successful procedures that can relieve pain and restore mobility for people with severe arthritis. Occasionally, joint replacement fails, and revision surgery is needed. Reasons for revision include infection, implant loosening, dislocation, and fracture. Warning signs of a problem include persistent pain, swelling, or instability. Revision surgeries are more complex, require longer recovery, and carry higher risks than the original surgery. Experienced surgeons who perform these procedures frequently tend to have the most success.
Walking, cycling, and swimming are best exercises for knee osteoarthritis
An analysis of 217 trials found that lower-impact aerobic exercise (walking, cycling, and swimming) is most effective for easing knee osteoarthritis pain and improving function. Other exercise types, such as flexibility, mind-body, neuromotor, and strengthening, also offer benefits.
Skipping breakfast may increase risk for metabolic syndrome
In a 2025 study, skipping breakfast was associated with a 10% increased risk for metabolic syndrome, a disorder defined by having three or more of the following: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high triglycerides, and low HDL cholesterol.
Coping with dry eyes
Dry eye disease is broken down into two types: In aqueous-deficient dry eye, the eyes don't produce enough tears. In evaporative dry eye (sometimes called meibomian gland dysfunction) there are enough tears, but they're unstable and evaporate too quickly. Dry eye symptoms include eyes that feel gritty, sandy, stinging, burning, scratchy, tired, or sensitive to light. People with symptoms often forgo seeing a doctor. Artificial tears are an effective starting point for many cases of dry eye.
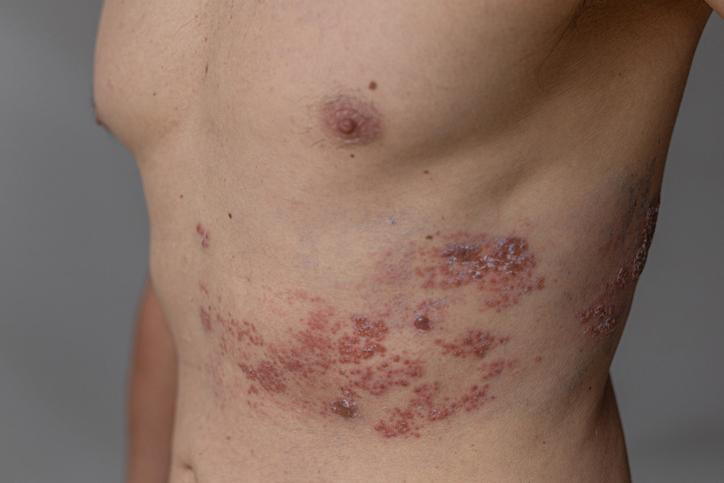
What to do if you have - or suspect you have - shingles
Shingles occurs when the dormant chickenpox virus reactivates, causing tingling, burning, and a painful, blistering rash. Shingles can affect anyone who has had chickenpox, with higher risk after age 50 and in people with weakened immunity. Diagnosis and treatment within three days of the rash appearing can shorten the illness and reduce severity. Most people recover completely from shingles, but there may be complications, such as post-herpetic neuralgia, which is pain that can be severe and long-lasting. Vaccination is the best way to prevent shingles and its complications.
Tips to cope when hearing hurts
Hyperacusis describes sensitivity to some or all sounds, no matter the volume. Depending on the person, sounds might be uncomfortably loud; cause pain in the ear, head, or another part of the body; trigger negative emotional responses; or make someone dizzy. These reactions might be due to irritated or overactive nerve fibers or muscles in the ear. While doctors have few treatments for hyperacusis, certain strategies help, such as avoiding sound triggers, wearing hearing protection, and engaging in sound therapy.
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) tied to heart problems
A 2025 study suggests that respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) can lead to heart-related complications, such as a heart attack, chronic heart failure, or an irregular heartbeat-even in people without a previous heart condition.

Aldosterone overload: An underappreciated contributor to high blood pressure

Can you retrain your brain to stop excessive drinking?

Beyond statins: New ways to lower LDL cholesterol

What is a cardioversion procedure?

Waking up to urinate at night affects blood pressure

Reversing prediabetes may slash heart disease risk by half

For now, electric cars appear safe for people with implanted heart devices

Finding and fixing a stiff, narrowed aortic valve

Can you stop blood thinners after an ablation for atrial fibrillation?

VO2 max: What it is and how you can improve it
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up