New thinking about plaque in arteries that feed the brain

Want to prevent shifting teeth? Maybe you need retainers

What you need to know about the new dietary guidelines

Food that’s healthier for people and planet can be cheaper, too

New evidence that polyphenol-rich foods help the heart

8 simple ways to reduce ultra-processed foods in your diet

How to curb your stress eating

How to spot Parkinson’s disease symptoms

Heart failure symptoms in women: How they’re different

GERD diet: Foods to avoid to reduce acid reflux
Colorectal Cancer Archive
Articles
Colorectal cancer screening before age 50?
Don’t wait until you turn 50 to screen for colon cancer
According to a new guideline, testing should start at age 45, but not everyone needs to have a colonoscopy. Other tests are also available.
Colon cancer screenings for people at average risk for the disease should start at age 45 instead of 50, says a new guideline from the American Cancer Society (ACS).
The change to the screening recommendation, which was published in the May 30 issue of CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, was made because the number of colon cancer cases among adults under age 55 rose 51% from 1994 to 2014, and colon cancer deaths in this age group rose 11% from 2005 to 2015.
Screening can often prevent colon cancer
Research we're watching
Image: © Catherine Lane/Getty Images
March is National Colorectal Cancer Awareness month. Have you been screened? Colon cancer is the second leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States, but is also highly preventable through recommended screenings. These screenings enable doctors to spot precancerous lesions that can lead to colon cancer and remove them before they become a problem. Screenings can also find cancers early, when they are most treatable. All people ages 50 to 75 should get recommended colon cancer screenings. Some people should start getting screened earlier if they have certain risk factors for colon cancer, including a family history, a personal history of inflammatory bowel disease (such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis), or a genetic condition that makes colon cancer more likely (such as familial adenomatous polyposis).
There are several tests used for colon cancer screening, including colonoscopy, which uses a device to examine the full length of the colon and rectum; stool tests; flexible sigmoidoscopy, which uses a device to examine a portion of the colon; and CT colonography, a scanning technique that produces images of the colon that are examined by the doctor.
Are colon cancer screenings necessary after a certain age?
On call
Q. I am 77 and in overall good health. My previous colonoscopies to check for colon cancer have been normal. Can I stop having them?
A. The major benefit of colon cancer screening is seen in men ages 50 to 75. After age 75, the potential benefit is smaller, and the risks and side effects of the procedure — like bleeding and perforation of the colon — are higher.
A new look at colon cancer screening
Don't be intimidated about screening tests. The latest guidelines suggest you can choose from multiple strategies.
Image: Bigstock
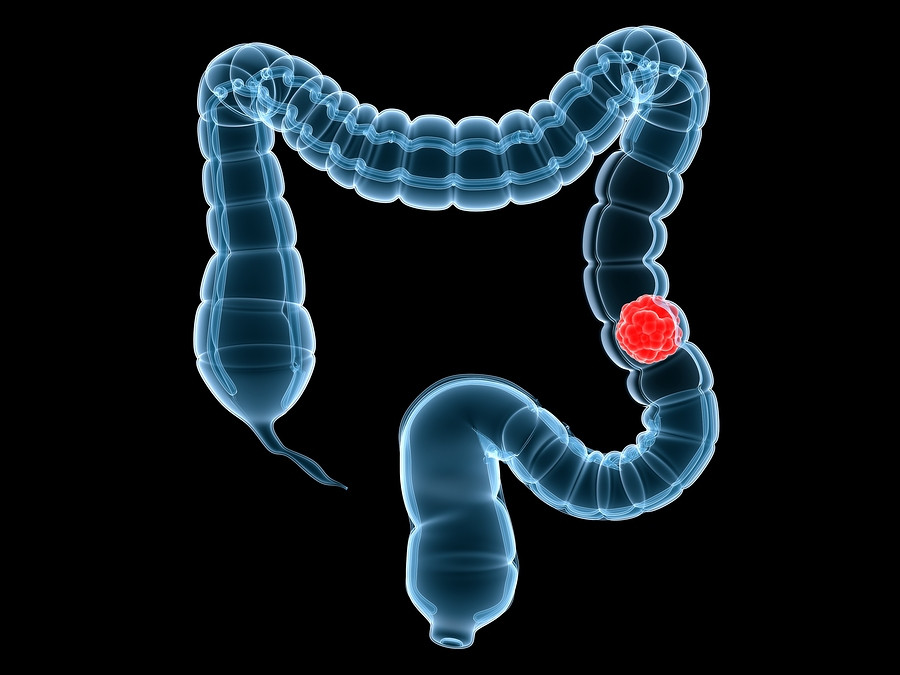
Colon cancer continues to be the country's second leading cause of cancer-related deaths and the third most common cancer in men, according to the CDC.
It almost always develops from precancerous polyps (abnormal growths). Screening tests, which are recommended for men ages 50 to 75, help find and sometimes aid removal of polyps before they become cancer. (Men older than 75 may still benefit, depending on their health.)
Adapting to life after cancer
Once you've completed treatment, adjusting to a "new normal" can be challenging.
Image: RuslaGuzov/ Thinkstock
Completing cancer therapy can feel like a graduation. You've done some hard work, it's paid off, and you may be ready to celebrate. But saying goodbye to treatment can arouse many of the emotions and uncertainties associated with beginning a new chapter in life.
Dr. Larissa Nekhlyudov is a general internist who works with cancer survivors at two Harvard affiliates, Brigham and Women's Hospital and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. She acknowledges that cancer survivors have a lot to deal with. "Once you've had your final chemotherapy infusion or swallowed the last pill, you may find yourself facing a new set of challenges—monitoring yourself for signs of recurrence, getting recommended follow-up care, adjusting to the long-term effects of treatment, psychologically adapting to normal life, and working to stay in good health," Dr. Nekhlyudov says.
Harvard researchers link coffee with reduced colon cancer recurrence
Image: Thinkstock |
You may drink coffee because it tastes good or helps you wake up. But the popular brew is also associated with health benefits, such as reducing the risk for heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. Now a study from Harvard-affiliated Dana-Farber Cancer Institute published Aug. 17, 2015, in the Journal of Clinical Oncology suggests that regular consumption of caffeinated coffee may be associated with a reduced recurrence of colon cancer, and even a reduced risk of death. The study included nearly 1,000 people with stage 3 colon cancer. They filled out questionnaires about their dietary patterns during chemotherapy, and then again six months after treatment was completed. People who drank four or more cups of coffee per day were 42% less likely to have cancer return than non-coffee drinkers, and were 34% less likely to die from cancer or any other cause.
This type of study doesn't prove that coffee drinking caused the lower chance of cancer recurrence and death. A randomized trial is needed to show cause and effect. But researchers are encouraged by the results. "Regular coffee intake has been associated with a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes, and it may be that through a similar mechanism, coffee may also improve outcomes for people with advanced colon cancer," says Dr. Charles Fuchs, senior author on the paper.
Ask the doctor: New DNA-based test for colorectal cancer
Q. I heard that there is a new stool test for colon cancer screening. Can this test replace colonoscopy for me? I am 68 years old with no history of colon problems, and my last colonoscopy was normal.
A. Among screening tests for hidden colorectal cancer, colonoscopy remains the "gold standard" because it's the most effective technique for detecting colon cancers and simultaneously provides an opportunity to remove any precancerous growths (polyps). The new DNA-based stool test (Cologuard) is less invasive and inconvenient than colonoscopy and finds more cancers and polyps than older stool tests, but it does not entirely eliminate the need for colonoscopies.
Switching to a fiber-rich diet may lower colon cancer risk in blacks
Switching from a “Western” diet with lots of fat and meat to a fiber-rich diet for just two weeks makes conditions in the large intestine less favorable to the development of colon cancer. The opposite switch may promote the formation of cancer. That’s the conclusion from a small but elegant study done in urban Pittsburgh and rural KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. In the study, 20 volunteers from each area switched diets. For two weeks, the Americans ate a traditional high-fiber African diet rich in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and beans, while the Africans ate a Western diet with more fat, protein, and meat. In just two weeks, significant changes occurred in the lining of the colon and in its chemical and bacterial make-up in both groups, but in different directions. Those following the African diet showed improvements in colon health likely to protect against colon cancer, while those following the Western diet showed changes that could lead to colon cancer.

New thinking about plaque in arteries that feed the brain

Want to prevent shifting teeth? Maybe you need retainers

What you need to know about the new dietary guidelines

Food that’s healthier for people and planet can be cheaper, too

New evidence that polyphenol-rich foods help the heart

8 simple ways to reduce ultra-processed foods in your diet

How to curb your stress eating

How to spot Parkinson’s disease symptoms

Heart failure symptoms in women: How they’re different

GERD diet: Foods to avoid to reduce acid reflux
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up