What are somatic workouts?

How to curb your stress eating

How to spot Parkinson’s disease symptoms

8 simple ways to reduce ultra-processed foods in your diet

Heart failure symptoms in women: How they’re different

GERD diet: Foods to avoid to reduce acid reflux

Strong is the new skinny

Everyday habits that sneakily weaken your bones

Don’t wait to get help for back pain

Correcting how you walk may ease osteoarthritis knee pain
Staying Healthy Archive
Articles
Do financial incentives improve health?
Ask the Doctor
Most large employers now offer financial incentives to workers who make healthy lifestyle changes.
Image: PHOTOS.com/Thinkstock
Q. My employer is offering employees financial rewards if we lose weight. At first, I was shocked by this, but then I thought it might be a good thing for me, and for my employer. Does this kind of financial incentive lead to healthier lifestyles?
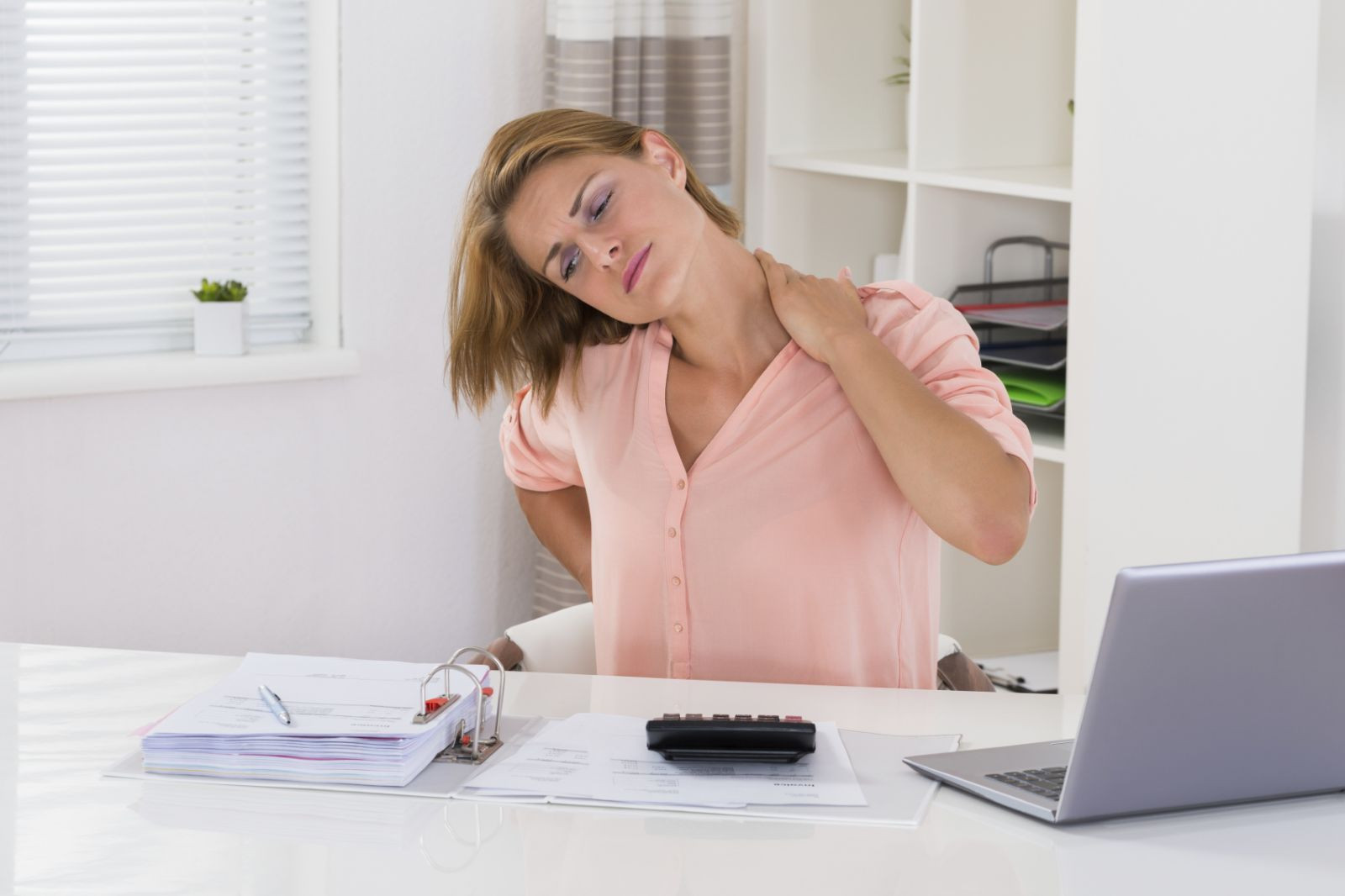
Do habits cause your neck pain?
Sit up straight, keep electronic screens at eye level, and try some strengthening exercises to reduce pain and feel better.
Looking down at a computer screen for prolonged periods may lead to neck pain.
Image: AndreyPopov/iStock
If your day involves using a smartphone or laptop, reading a book or magazine, or curling up on a couch to watch TV, your day may also include some nagging neck pain. That's because you may be bending your body in an unhealthy position for a prolonged period of time. "It's an overuse injury. Your body was designed to move, but you're forcing your neck and shoulders into one static position for too long," says Dr. Clare Safran-Norton, a physical therapist and clinical supervisor of rehabilitation services at Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women's Hospital.
Spice up your dinner with foreign flavors
Indian, Peruvian, or Vietnamese food may be just the thing to give your diet a dose of interest and fun.
Vietnamese pho with shrimp is tasty. But stick to small portions of noodles to avoid spiking blood sugar.
Image: joannatkaczuk/Thinkstock
Following a healthy diet doesn't have to be boring. Take your palate on a culinary adventure by sampling world cuisines that are new to you. "Variety can add taste as well as vitamins and micronutrients you may not be receiving from your standard diet," says registered dietitian Kathy McManus, director of the Department of Nutrition at Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women's Hospital.
What you need to know if you’re taking multiple medications
To stay on your regimen, you'll have to be organized and learn about each of your drugs.
Many older adults take five or more prescription medications, increasing the risk of harmful drug interactions.
Image: Comsstock/Thinkstock
Taking several types of medications can be challenging. But this is something you have to get right. If you don't, you may have unwanted side effects, or you may not properly treat your chronic condition. "I see people who average 15 medications, and it's very difficult for them to juggle that many pills," says Joanne Doyle Petrongolo, a pharmacist at Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts General Hospital.
Harvard study links aspirin therapy and cancer prevention
News Briefs
Image: DimaSobko/Thinkstock
A Harvard study published March 3, 2016, in JAMA Oncology adds to increasing evidence that aspirin use may help stave off colorectal cancer and suggests that aspirin is also associated with a small reduction of overall cancer risk.
Researchers looked at aspirin use among almost 136,000 men and women in two studies over 32 years. They noted that regular aspirin use—taking either a 325-mg tablet or an 81-mg tablet two or more times per week—was associated with a 3% reduction in cancers over all, although they saw no effect on major cancers like those of the breast, prostate, or lung. The researchers say the overall reduction was due mostly to a 15% risk reduction for gastrointestinal cancer and a 19% risk reduction for colorectal cancer.
New guidelines: Avoid opioids for chronic pain
News Briefs
The CDC wants doctors to stop treating chronic pain by prescribing opioids, such as oxycodone (OxyContin). The CDC published guidelines on opioid prescription March 15, 2016, in The Journal of the American Medical Association. Opioids are powerful painkillers typically used to treat severe pain after surgery or pain with terminal illness, and sometimes used to treat chronic pain. But long-term use of these drugs comes with the risk of dependence, addiction, overdose, and death, as we reported in March.
The CDC is recommending that doctors instead treat chronic pain with non-opioid painkillers, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil); anticonvulsants (gabapentin or pregabalin); tricyclic antidepressants; or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors. The CDC also suggests treating chronic pain with nondrug therapies, such as physical therapy. If you and your doctor feel the benefits of opioid therapy outweigh the risks, the CDC urges doctors to prescribe the lowest effective dose, and reassess risks and benefits at least every three months. The recommendation is not intended for people taking opioids for terminal illness or palliative care.
Medication-free options to treat your low back pain
News Briefs
Image: Moldboard/Thinkstock
A small study published in March 2016 in The Journal of the American Medical Association appears to support two nondrug options for treating chronic lower back pain. Researchers found that mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR), which includes yoga and mindfulness meditation (focusing on the moment), and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), which redirects pain-related thoughts and behaviors, were better at lowering back pain than usual care (other treatments received, if any).
Researchers randomly assigned more than 300 people (average age 49) to usual care or to eight weekly sessions of either MBSR or CBT. Six months later, researchers found that 45% of both the MBSR and CBT groups had less back pain, compared with 27% of the usual-care group, and about 60% of both MBSR and CBT participants had more back function, compared with 44% of those getting usual care.
Shopping for sunglasses
Wearing lenses that screen out harmful ultraviolet radiation is essential for keeping your eyes healthy.
Large wraparound lenses offer the best protection.
Image: Wavebreakmedia/Thinkstock
When you buy sunglasses, your primary aim might be to find a style that looks good on you and is comfortable. If so, like almost half of people selecting sunglasses from the racks, you've failed to consider the most important detail—the amount of harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation the lenses screen out.
Debunking misconceptions around addiction
Dr. Michael Bierer explains the most common misconception about addiction and offers tips for recognizing if you might be developing an addiction.
Treatments for opioid medication addictions
Dr. Wynne Armand talks with Dr. Terry Schraeder about the increase in opiod addictions and shares prevention and treatment methods for those experiencing an addiction to prescription opioid medication.

What are somatic workouts?

How to curb your stress eating

How to spot Parkinson’s disease symptoms

8 simple ways to reduce ultra-processed foods in your diet

Heart failure symptoms in women: How they’re different

GERD diet: Foods to avoid to reduce acid reflux

Strong is the new skinny

Everyday habits that sneakily weaken your bones

Don’t wait to get help for back pain

Correcting how you walk may ease osteoarthritis knee pain
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up