5 timeless habits for better health

What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?

Is your breakfast cereal healthy?

When pain signals an emergency: Symptoms you should never ignore

Does exercise give you energy?

Acupuncture for pain relief: How it works and what to expect

How to avoid jet lag: Tips for staying alert when you travel

Biofeedback therapy: How it works and how it can help relieve pain

Best vitamins and minerals for energy

Should you take probiotics with antibiotics?
Osteoporosis Archive
Articles
Protecting the skin from the sun doesn't increase fracture risk
Protecting the skin from the sun doesn't increase the risk of vitamin D deficiency or bone fracture, according to a recent study.
5 ways to boost bone strength early
The best prevention for bone-thinning osteoporosis begins early — during the first two decades of life, when you can most influence your peak bone mass by getting enough calcium and vitamin D and doing bone-strengthening exercise. If you are over age 20, there's no need to be discouraged. It's never too late to adopt bone-preserving habits.
If you are a man younger than 65 or a premenopausal woman, these five strategies can help you shore up bone strength as a hedge against developing osteoporosis.
Eczema is associated with a higher risk of bone breaks
Research we're watching
If you suffer from the common skin condition eczema, you may have a higher risk of breaking a bone compared with someone who doesn't have the condition, according to a study published in the February 2020 issue of The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. The study authors found that the 500,000 people in the study who had eczema, which causes itchy dry patches on the skin, were 7% to 18% more likely to break a bone in the wrist, hip, pelvis, or spine when compared with more than 2.5 million participants who didn't have the condition. Researchers said it's not clear if this elevated fracture risk was related to the eczema itself or whether other factors caused the association. For example, the increase in risk could have been related to medications people took to treat eczema. Even so, if you have eczema, the study authors say it may be worth asking your doctor whether you might be at increased risk for osteoporosis.
Image: © vadimguzhva/Getty Images
Boning up on osteoporosis
Men need to manage their bone health as much as women do.
Most people think of osteoporosis as a women-only health problem, but older men also need protection from this bone-weakening disease.
About one in four men older than 50 will break a bone because of osteoporosis during his lifetime, according to the National Osteoporosis Foundation. And research has found that compared with women, older men are more likely to die following a fracture related to osteoporosis.
What’s the best time of day to take your medication?
Timing may improve potency and help you cope with side effects.
We all want our medicines to be as effective as possible, and that requires effort on our part. It may be necessary to avoid taking pills with certain foods or drinks, and to check that medications won't interfere with each other.
And in some cases, it may be important to take a drug at a particular time of day. This approach, known as chronotherapy, is gaining attention as research suggests a relationship between when we take medications and how well they work.
Good for your teeth, bad for your bones?
Could an ingredient in toothpaste be harmful to your bones? Triclosan, an antibacterial agent, has been banned from soaps and hand sanitizers by the FDA, and researchers have found that women with the highest levels of triclosan in their urine had low bone density measurements.
Can I do anything to prevent osteoporosis?
Ask the doctors
Q. I know that osteoporosis is linked to hereditary factors that I can't change. But are there things I can do to reduce my risk?
A. It's true that many risk factors for osteoporosis, such as your sex, age, and genes, are not things you can change. But there are things you can do to improve your bone health. This includes adopting a healthy diet that is rich in calcium and getting enough vitamin D, which can help maintain and improve bone health. Regular exercise can also help strengthen your bones or prevent bone loss. In particular, activities that put stress on your bones, such as jumping, running, and weight-bearing exercises, can stimulate bone cells to produce proteins that bolster bone strength. In children, these activities can actually increase bone density. While adults don't gain the same degree of benefit that kids do, exercise can still have moderate effects on bone, helping to maintain strength that might otherwise be lost. To further protect bone health, cut down on unhealthy habits, such as smoking or drinking excess amounts of alcohol. If you have risk factors for osteoporosis, you might also want to talk to your doctor about whether any of your medications might be harming your bone health.
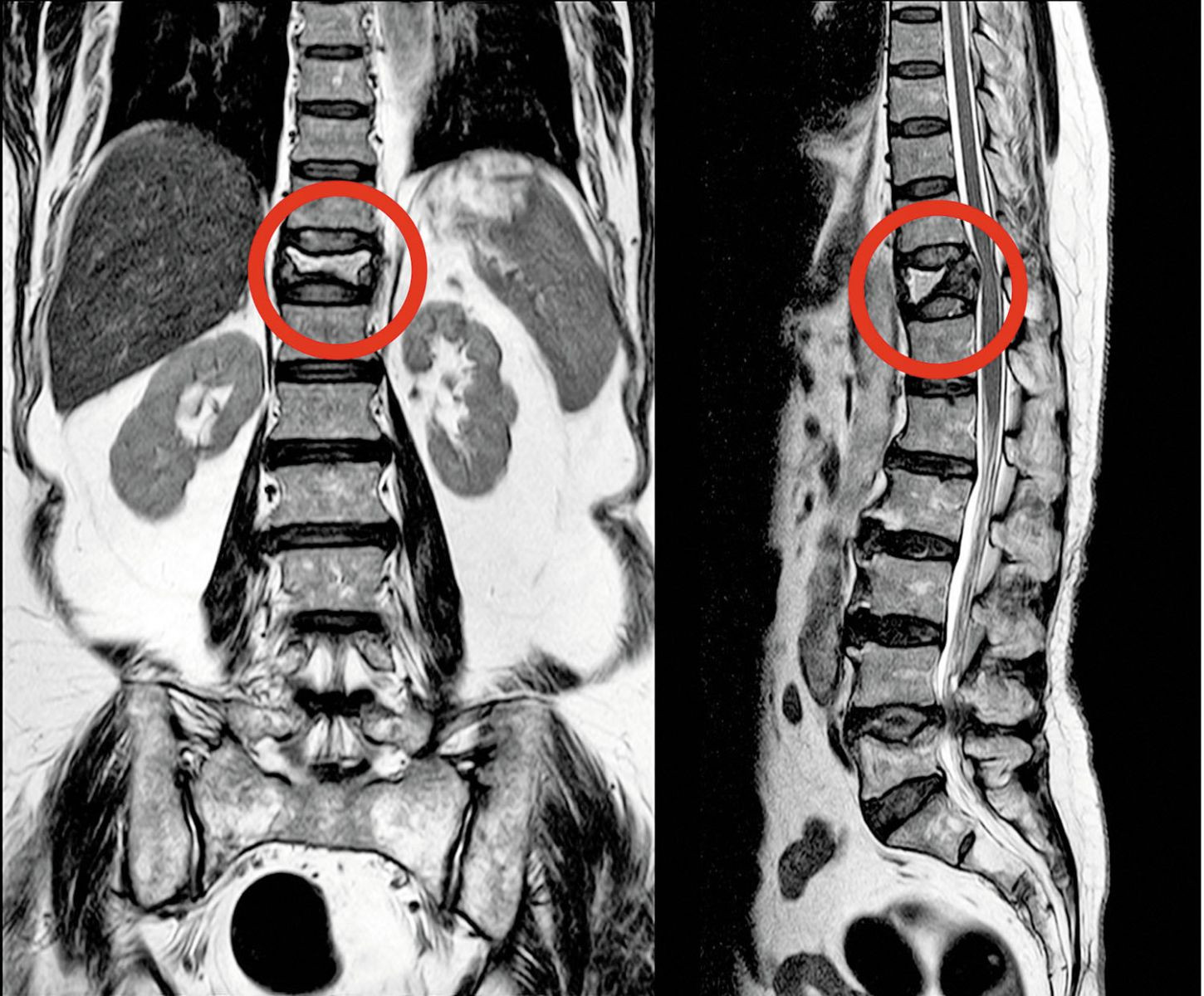
A broken back without the fall
Don't ignore back pain, height loss, or osteoporosis. They could be signs of a compression fracture.
You didn't fall, and you didn't do anything strenuous. So it may come as a surprise when the bad back pain you've been experiencing turns out to be one or more broken bones in your back. "A common story is that someone bends down to put something in the dishwasher or steps off a curb a little hard and puts additional load on their spine. The weakened bone is not adequate to take that load, and it collapses," says Dr. Julia Charles, a rheumatologist and bone cell researcher at Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women's Hospital.
What weakens the spine?
Your spine contains about 30 bones called vertebrae, stacked on top of each other like a roll of quarters. Each vertebra consists of an external bone surface (like plaster), and an inside filled with a honeycomb of support rods called trabeculae.
A new therapy for osteoporosis: Romosozumab
Osteoporosis affects 10 million people in the United States, the majority of them women. Romosozumab is a new type of medication for treating osteoporosis that offers another treatment option for some women after menopause.

5 timeless habits for better health

What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?

Is your breakfast cereal healthy?

When pain signals an emergency: Symptoms you should never ignore

Does exercise give you energy?

Acupuncture for pain relief: How it works and what to expect

How to avoid jet lag: Tips for staying alert when you travel

Biofeedback therapy: How it works and how it can help relieve pain

Best vitamins and minerals for energy

Should you take probiotics with antibiotics?
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up