Trying to lose weight? Be careful not to lose muscle
Is your skin problem actually an autoimmune condition?

People with diabetes face higher risk of hearing loss

Antibiotic-free fixes for recurrent UTIs

Musculoskeletal syndrome of menopause: When menopause makes you ache all over
When can older women stop getting mammograms?

To lose weight, especially harmful belly fat, combine diet and exercise

Can men hold off on treating recurring prostate cancer?

The 7 types of rest and why we need them all

What are the early warning signs of cervical cancer?
Osteoporosis Archive
Articles
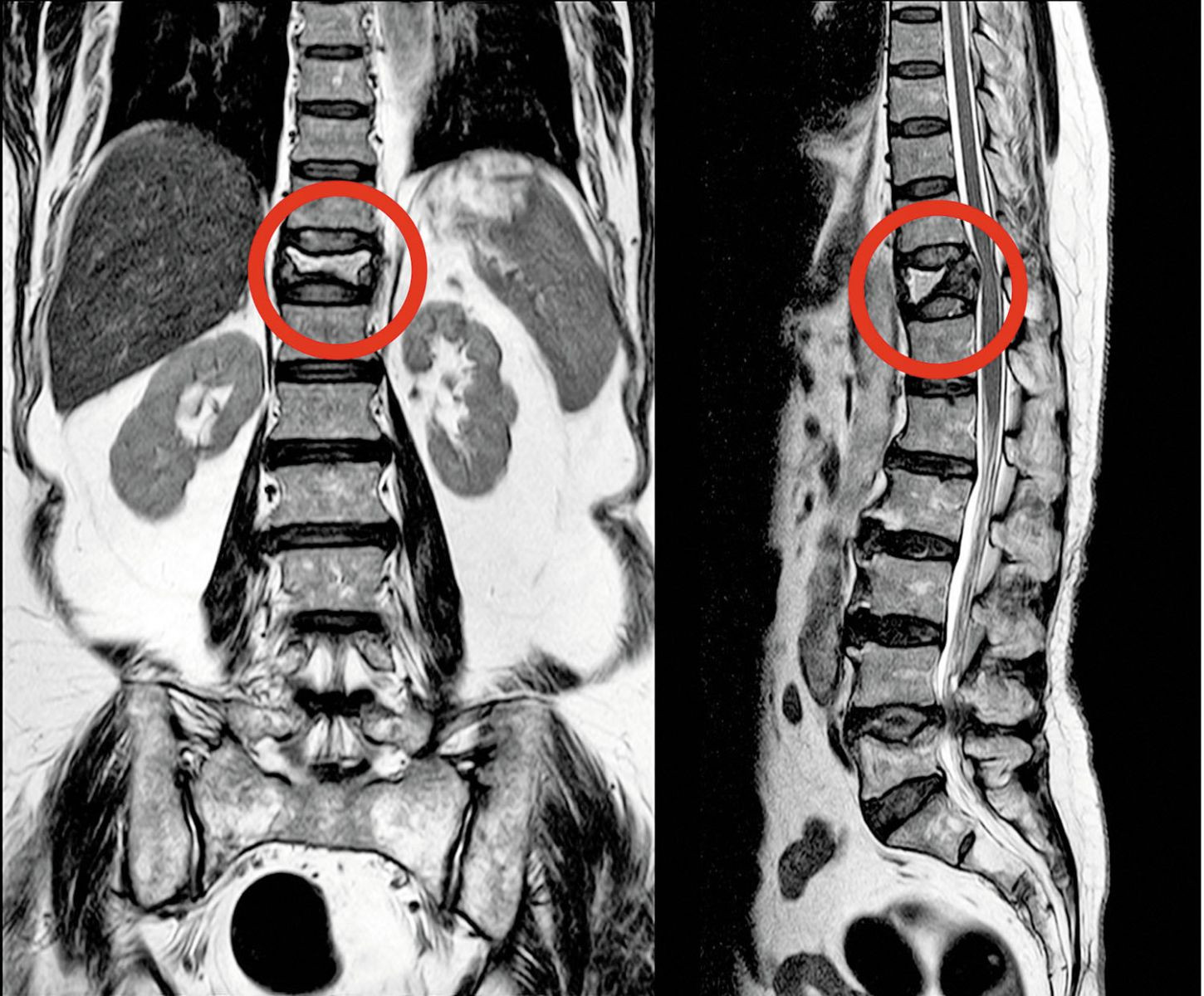
A broken back without the fall
Don't ignore back pain, height loss, or osteoporosis. They could be signs of a compression fracture.
You didn't fall, and you didn't do anything strenuous. So it may come as a surprise when the bad back pain you've been experiencing turns out to be one or more broken bones in your back. "A common story is that someone bends down to put something in the dishwasher or steps off a curb a little hard and puts additional load on their spine. The weakened bone is not adequate to take that load, and it collapses," says Dr. Julia Charles, a rheumatologist and bone cell researcher at Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women's Hospital.
What weakens the spine?
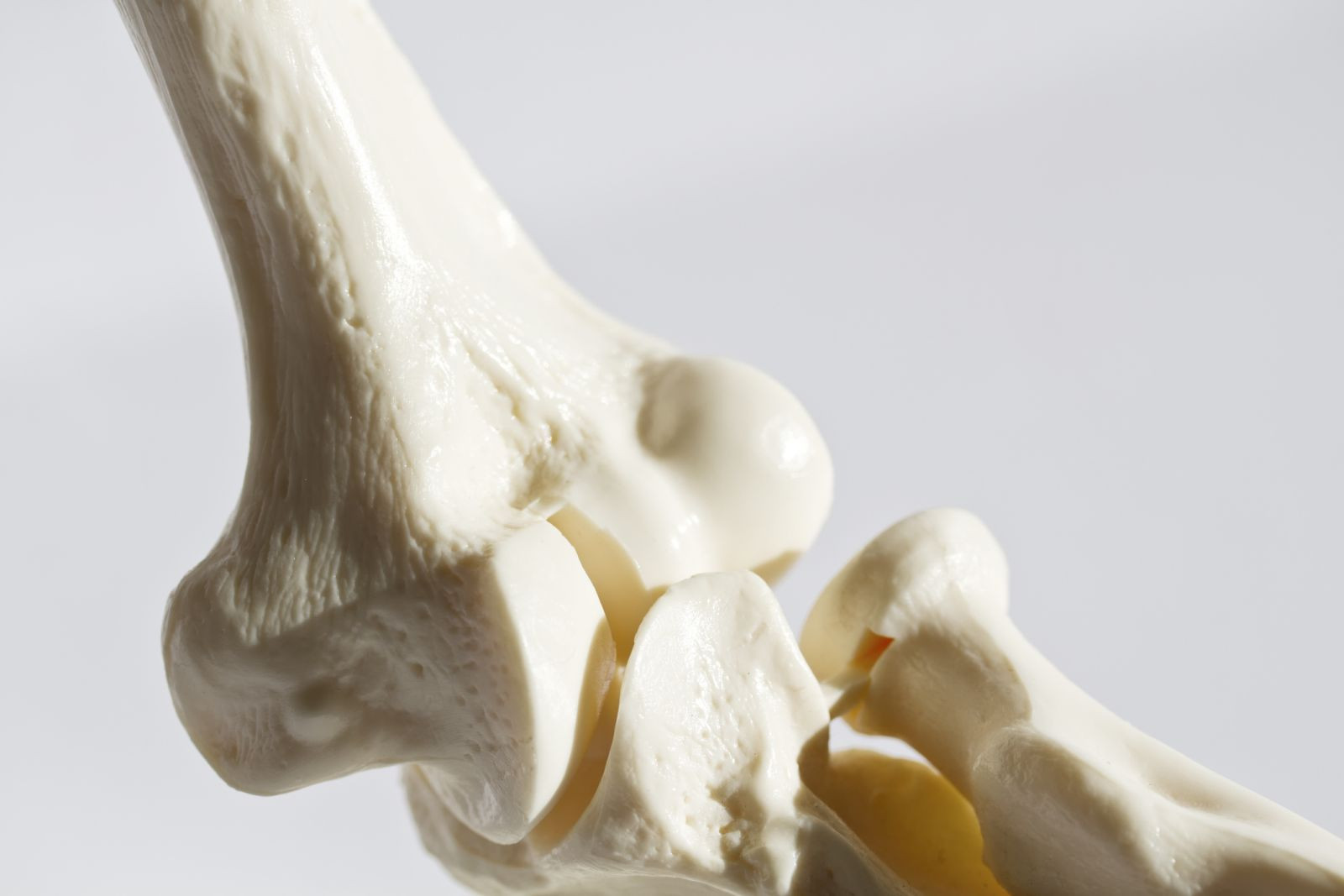
Your spine contains about 30 bones called vertebrae, stacked on top of each other like a roll of quarters. Each vertebra consists of an external bone surface (like plaster), and an inside filled with a honeycomb of support rods called trabeculae.
A new therapy for osteoporosis: Romosozumab
Osteoporosis affects 10 million people in the United States, the majority of them women. Romosozumab is a new type of medication for treating osteoporosis that offers another treatment option for some women after menopause.
Taking osteoporosis drugs shouldn't prevent you from getting oral surgery
A drug holiday is one recommendation to reduce the risk of a rare bone condition that affects the jaw.
A dentist refers a woman to an oral surgeon because she needs a tooth pulled. But upon reviewing her chart, the oral surgeon turns her away.
The reason? She's taking a common medication to treat her osteoporosis, a condition that causes bones to become thin, brittle, and prone to fracture.
Keeping bones strong
Ounce for ounce, bone bears as much weight as reinforced concrete. However, unlike reinforced concrete, bone is a living tissue. It serves as a repository of minerals for the rest of the body to use, continuously lending them out and replacing them. Bone also gets stronger when "stressed" by physical activity, and can repair itself when injured.
The building and tearing down of bone tissue is called remodeling. This process happens continuously throughout your entire life. At first, your body rebuilds more bone than it demolishes. Typically, a person reaches peak bone mass around the age of 30. Among women, bone mass usually remains steady for the next 20 years or so until the onset of menopause, when bone is lost much more quickly than it is replaced. When bone loss is significant, the result is osteoporosis (which means "porous bone"). Bone loss generally starts later for men — typically in the late 50s — and progresses more slowly than in women. But men can also get osteoporosis.
Does osteoporosis cause any symptoms?
Ask the doctors
Q. Is there any way to tell if you are getting osteoporosis? Are there symptoms?
A. Osteoporosis is a disease that causes your bones to become weak and brittle and more likely to break. Unfortunately, you probably won't have any symptoms until the disease is advanced or you actually experience a fracture. However, there are two visible clues of osteoporosis: changes in your posture (such as a hunched-over appearance) and loss of height. Both of these changes may be caused when your spine becomes curved or compressed from weakness or tiny fractures (called compression fractures) in your vertebrae, the small bones that make up your spine.
Two keys to strong bones: Calcium and Vitamin D
Image: memoriesarecaptured/Thinkstock
Although bone-weakening osteoporosis is quite common among older people, it isn't an inevitable part of aging. There's a lot you can do to shield your bones from this disease.
The best insurance against osteoporosis is building the highest bone density possible by your 30s and minimizing bone loss after that. But if you you're already in midlife or beyond, there is still much you can do to preserve the bone you have and perhaps even to replace lost bone. Daily weight-bearing exercise, like walking, is the best medicine. Getting enough calcium and vitamin D are two other critical strategies for keeping bones strong.
Why middle-age spread is a health threat
Those extra inches around the middle may signal increased fat around abdominal organs and rising health risks.
It's a rare woman over age 50 who has the same waist measurement she had as a teenager. But in the past decade or so, women's waistlines have been expanding regardless of age. A 2014 report from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey found that from 1999 to 2012, the average body mass index (BMI) for women age 20 or older held steady. But during the same period, the average female waistline grew slowly and steadily, from 36.2 inches to 37.8 inches. Researchers are still searching for an explanation for this phenomenon, but they do know one thing: increasing waistlines are linked to greater risks for heart disease, diabetes, and osteoporosis.
What's in a waistline?
Regardless of whether your weight has changed over the years, your height is likely to have decreased, the result of declining volume in the intervertebral discs of the spine. As your torso shortens, your abdominal organs have less vertical space to inhabit, so they move horizontally. If you haven't gained weight, an increase of an inch or two around the waist may simply reflect lost height.
Ask the doctor: Why would I need Prolia?
Denosumab (Prolia) is recommended for people at high risk for fractures for whom other bone-loss treatments were ineffective or had intolerable side effects.
Boning up on osteoporosis
The disease strikes more women, but men are also at risk.
Osteoporosis is often considered a woman's disease, but men also need to be concerned about this bone-weakening condition. About 2 million men have osteoporosis and another 12 million are at high risk, according to the National Osteoporosis Foundation.
In fact, older men have a greater risk for an osteoporosis-related fracture than for getting prostate cancer, and about one in four men older than 50 will break a bone because of osteoporosis during his lifetime.

Trying to lose weight? Be careful not to lose muscle

Is your skin problem actually an autoimmune condition?

People with diabetes face higher risk of hearing loss

Antibiotic-free fixes for recurrent UTIs

Musculoskeletal syndrome of menopause: When menopause makes you ache all over

When can older women stop getting mammograms?

To lose weight, especially harmful belly fat, combine diet and exercise

Can men hold off on treating recurring prostate cancer?

The 7 types of rest and why we need them all

What are the early warning signs of cervical cancer?
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up