Driving with arthritis pain: Stay comfortable — and safe — behind the wheel

Daily cup of coffee may prevent afib recurrence

Gene-editing therapy lowers harmful blood fats in early study

What is EMDR therapy, and who can it help?

GLP-1 drugs versus bariatric surgery for treating obesity

Two dumbbells, three exercises, and 10 minutes

Easing the emotional burden of IBS

Modify your push-ups to meet your fitness level

What is long QT syndrome?

Stroke survivors may benefit from very low LDL levels
Bladder & Bowel Archive
Articles
How to prep for a successful colonoscopy
Bowel preparation (prep) is considered the most unpleasant part of the colonoscopy process, but it’s also crucial. A clean bowel helps the gastroenterologist more easily locate and remove polyps, small growths that can develop into cancer. If the prep is inadequate, the patient will have to repeat the process. Updated guidelines for gastroenterologists, published in 2025, can help them guide their patients to have more successful preps.
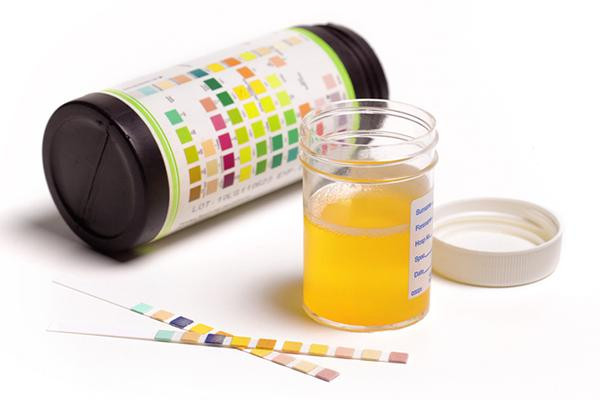
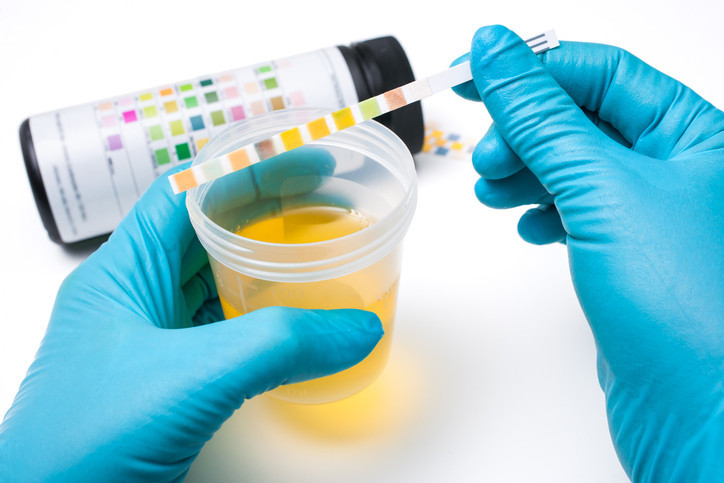
Urine and your health
A urine test, also known as a urinalysis, can reveal a great deal about a person’s health. The kidneys produce urine to remove excess fluid and waste products from the body. But urine also contains various chemicals, minerals, toxins, bacteria, and red and white blood cells. Analyzing a urine sample with visual, chemical, and microscopic exams can reveal the presence and amounts of these substances, which can provide clues to specific conditions.
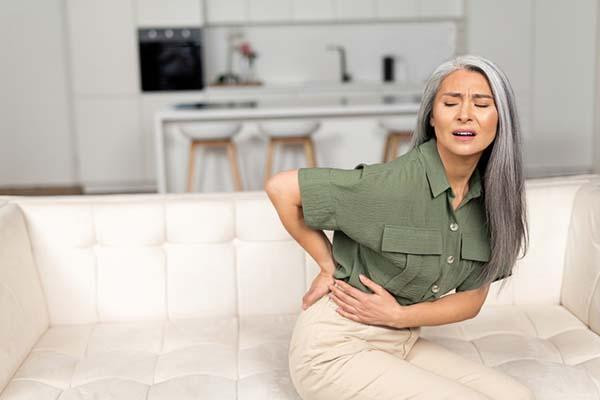
The overlap between back pain and pelvic floor dysfunction
Pelvic floor dysfunction in women is commonly linked to lower back pain. The odds of developing pelvic floor–related back pain increase for women as they get older due to factors such as diminished estrogen and childbirth-related pelvic floor damage. Lower back pain and pelvic floor dysfunction may also have overlapping signs, including urinary leakage or urgency, a feeling of heaviness in the pelvis or vaginal bulging, constipation or bowel issues, painful sex or urination, and pain with prolonged sitting or standing.
Are colon cleanses safe?
Colon cleanses are marketed to help detoxify the body, boost weight loss and immune function, and increase energy. But the colon removes toxins on its own. Colon cleanses also pose multiple health risks.

Driving with arthritis pain: Stay comfortable — and safe — behind the wheel

Daily cup of coffee may prevent afib recurrence

Gene-editing therapy lowers harmful blood fats in early study

What is EMDR therapy, and who can it help?

GLP-1 drugs versus bariatric surgery for treating obesity

Two dumbbells, three exercises, and 10 minutes

Easing the emotional burden of IBS

Modify your push-ups to meet your fitness level

What is long QT syndrome?

Stroke survivors may benefit from very low LDL levels
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up