Obesity appears not to raise risks from shoulder replacement surgery
News briefs
- Reviewed by Robert H. Shmerling, MD, Senior Faculty Editor, Harvard Health Publishing; Editorial Advisory Board Member, Harvard Health Publishing
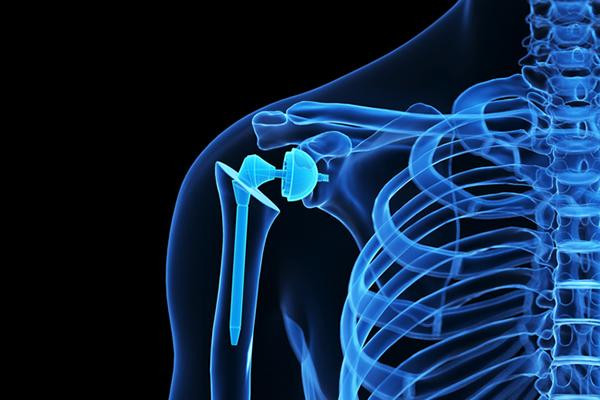
When people with severe arthritis in the shoulder find that nonsurgical treatments are no longer enough to manage pain and stiffness, shoulder replacement surgery can relieve the pain and restore use of this highly mobile joint.
All surgery comes with risks. With some joint replacement surgeries, especially knee and hip replacements, people with obesity have a higher risk of complications such as blood clots, infections, and poor wound healing. The increased risk is partially related to excess body weight, but people with obesity also often have other medical conditions, such as diabetes, which can raise risk of complications.
A study published Nov. 20, 2025, in PLOS One investigated the effects of body weight on surgical outcomes in more than 20,000 people undergoing elective shoulder replacement. The researchers found that compared to normal weight people, even people with a body mass index (BMI) of at least 40 (indicating severe obesity) did not have a greater risk for serious complications (including death) within 90 days, or for needing another surgery within 4.5 years. Few people in the study were underweight (BMI less than 18.5), but they appeared to have the highest risk of complications compared to those with normal or heavier body weights.
Image: © Sebastian Kaulitzki/Science Photo Library/Getty Images
About the Author

Lynne Christensen, Staff Writer
About the Reviewer

Robert H. Shmerling, MD, Senior Faculty Editor, Harvard Health Publishing; Editorial Advisory Board Member, Harvard Health Publishing
Disclaimer:
As a service to our readers, Harvard Health Publishing provides access to our library of archived content. Please note the date of last review or update on all articles.
No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.