New thinking about plaque in arteries that feed the brain

Want to prevent shifting teeth? Maybe you need retainers

What you need to know about the new dietary guidelines

Food that's healthier for people and planet can be cheaper, too

New evidence that polyphenol-rich foods help the heart

How to spot Parkinson's disease symptoms

8 simple ways to reduce ultra-processed foods in your diet

GERD diet: Foods to avoid to reduce acid reflux

How to curb your stress eating

Heart failure symptoms in women: How they're different
Prostate Cancer Archive
Articles
A new treatment for advanced prostate cancer improves survival in phase 3 clinical trial
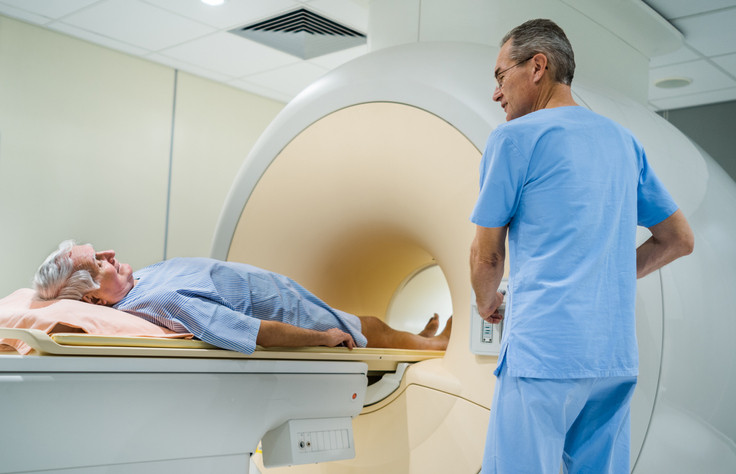
MRI looking better for detecting prostate cancer
American Heart Association issues statement on cardiovascular side effects from hormonal therapy for prostate cancer
New ways to test for prostate cancer
Recent advances can help men with a worrisome PSA result avoid immediate biopsy.
Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood testing receives high marks as an effective way to monitor disease activity in men diagnosed with prostate cancer. Yet, as a screening tool for prostate cancer, PSA testing is problematic.
PSA naturally tends to increase as men get older, but levels that get too high may suggest prostate cancer. A PSA level of less than 4 nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL) is often reassuring, unless there has been a sudden jump from a much lower number. Many doctors consider a total PSA level higher than 10 ng/mL as the threshold for getting a biopsy to check for cancer.
Predicting low-risk prostate cancer
New calculators can estimate the chance your cancer might — or might not — become more aggressive.
Active surveillance is a popular option for men with low-risk prostate cancer, defined as a tumor that is confined to the prostate gland and unlikely to grow or spread. It involves monitoring prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels in the blood for changes and having regular digital rectal exams to look for abnormal areas on your prostate.
During active surveillance, you have a PSA test and a digital rectal exam every six months and prostate biopsies approximately every other year. If your PSA level rises, your doctor will likely recommend a prostate MRI or an immediate prostate biopsy to see if the cancer has become more aggressive. If so, you and your doctor can decide whether to continue with active surveillance and have another biopsy six months or a year later, or move ahead to treatment, such as radiation, hormonal therapy, or surgery.
Radiation after prostate cancer surgery may not be necessary
In the journals
Many men with prostate cancer who have a radical prostatectomy (prostate removal) receive radiation therapy afterward to wipe out any residual cancer cells. Alternatively, men can choose to delay radiotherapy and be monitored for evidence of prostate cancer activity, such as a rising blood level of prostate-specific antigen (PSA). If PSA testing or an imaging test like an MRI shows cancer, these men can then consider radiation therapy.
According to the findings of an analysis published online Sept. 28, 2020, by The Lancet, there is no clear benefit of immediate radiation over monitoring with later radiation therapy as necessary. Since some men will never need radiotherapy, this means that by forgoing immediate treatment, they can avoid potential side effects like incontinence and bowel problems.
Hormone therapy and radiation may help with certain prostate cancer
In the journals
Men with intermediate-risk prostate cancer may benefit from undergoing androgen-deprivation therapy (ADT) depending on how far the cancer has progressed, says a study published online Sept. 9, 2020, by JAMA Network Open. The results could help men better weigh risk versus reward when choosing their prostate cancer treatment options.
The study looked at men with intermediate-risk prostate cancer. This is the mid-range of prostate cancer in terms of aggressiveness between low-risk (which often doesn't need treatment) and high-risk cancer. There are two categories of intermediate-risk cancer: favorable intermediate-risk (FIR) and the more advanced unfavorable intermediate-risk (UIR).
Combining two types of biopsies helps diagnose prostate cancer
In the journals
Combining two kinds of biopsies may lead to a more accurate diagnosis of prostate cancer, suggests a study in the March 5, 2020, issue of The New England Journal of Medicine. Researchers from the National Cancer Institute enrolled 2,103 men with prostate abnormalities. Each man had a standard 12-point biopsy and an MRI-targeted biopsy.
With a 12-point biopsy, tissue samples are taken from 12 systematically placed spots on the prostate. An MRI-targeted biopsy uses an MRI image of the prostate to help doctors locate areas where cancer is most highly suspected. Previous research has shown that MRI-targeted biopsies are more accurate than 12-point biopsies. However, even MRIs can miss some tumors.
The facts about testosterone and sex
Can boosting testosterone levels improve your sex life?
The hormone testosterone plays a big part in men's health, but perhaps its most meaningful role is to fuel sex drive and performance.
Testosterone levels tend to decrease with age. They peak by early adulthood and then can drop by up to 1% per year beginning around age 40. Sometimes an abrupt fall occurs because of an injury or illness (such as an infection), chemotherapy or radiation treatment, or certain medications.

New thinking about plaque in arteries that feed the brain

Want to prevent shifting teeth? Maybe you need retainers

What you need to know about the new dietary guidelines

Food that's healthier for people and planet can be cheaper, too

New evidence that polyphenol-rich foods help the heart

How to spot Parkinson's disease symptoms

8 simple ways to reduce ultra-processed foods in your diet

GERD diet: Foods to avoid to reduce acid reflux

How to curb your stress eating

Heart failure symptoms in women: How they're different
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up