Driving with arthritis pain: Stay comfortable — and safe — behind the wheel

Daily cup of coffee may prevent afib recurrence

Gene-editing therapy lowers harmful blood fats in early study

What is EMDR therapy, and who can it help?

GLP-1 drugs versus bariatric surgery for treating obesity

Two dumbbells, three exercises, and 10 minutes

Easing the emotional burden of IBS

Modify your push-ups to meet your fitness level

What is long QT syndrome?

Stroke survivors may benefit from very low LDL levels
Physical Activity Archive
Articles
A modest level of physical activity may help protect women from health risks
According to a 2025 study, women who walked at least 4,000 steps per day once or twice a week had a lower risk of cardiovascular disease and early death compared with women who did not reach this threshold.
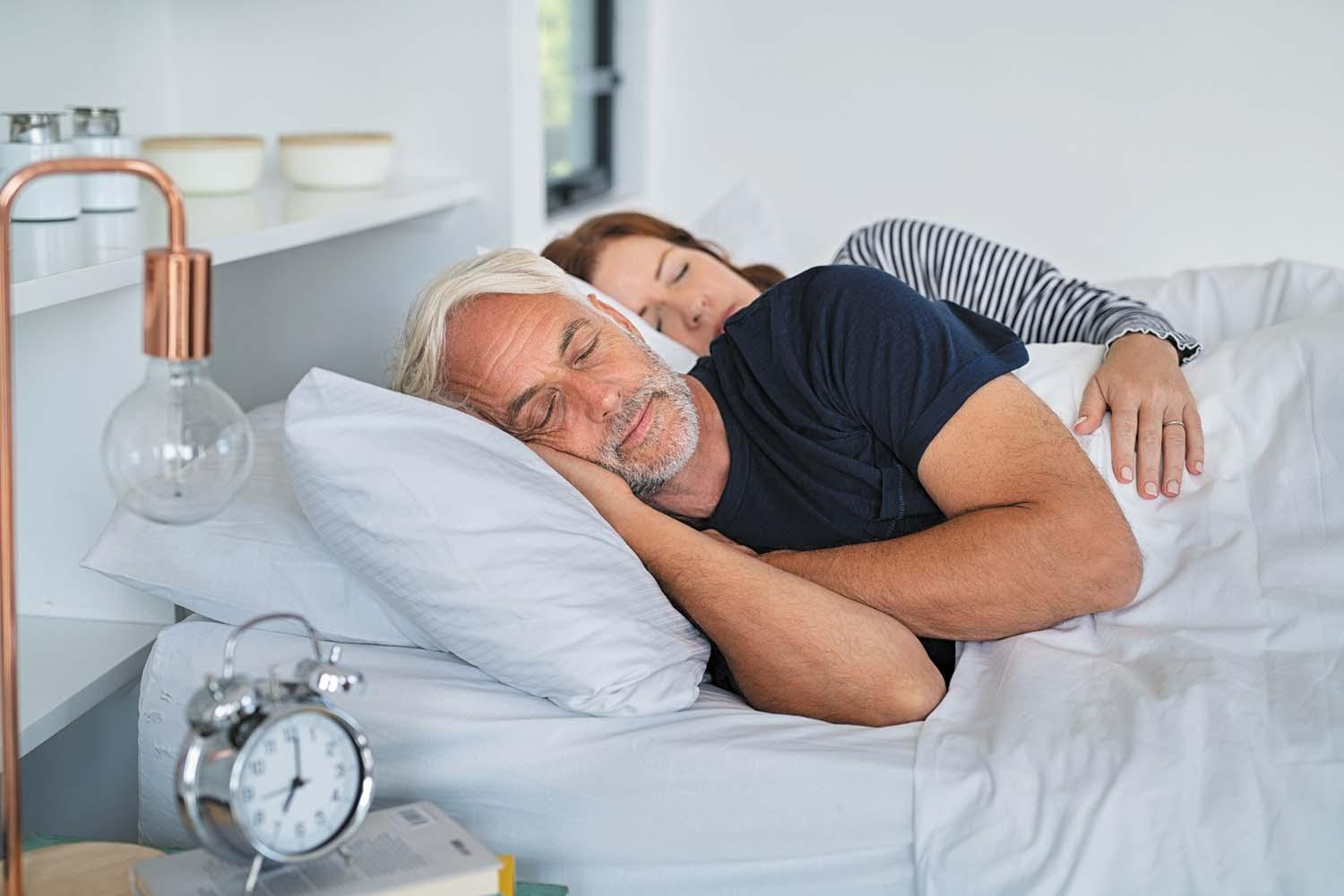
Does exercising in the evening affect sleep?
Research suggests that people can exercise in the evening without it affecting their sleep if they avoid physical activity several hours before bedtime.
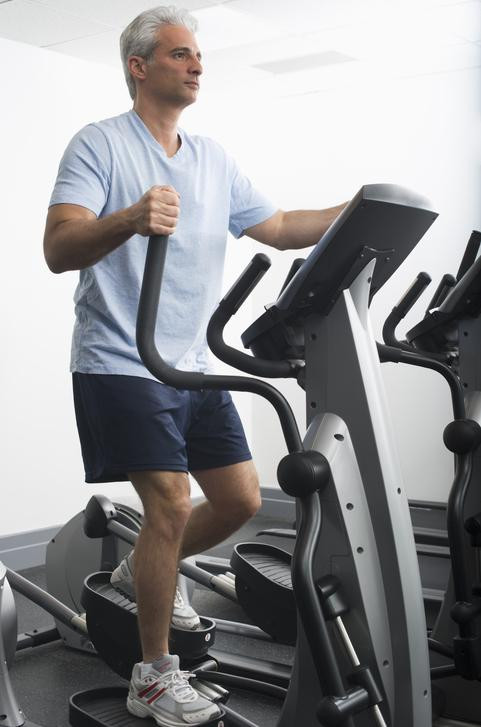
Why you should try ellipticals
Ellipticals are stationary exercise machines that simulate walking, running, or stair climbing. They combine cardio with strength training and can simultaneously engage the upper and lower body for a full-body workout. Ellipticals also offer a low-impact exercise, placing less stress on the knee, hip, and ankle joints, which make them ideal for people who have knee or hip osteoarthritis or are recovering from an injury.
A fresh approach to cardio exercises
There are many ways people can meet the national guidelines for weekly activity. While running and walking are popular exercise choices, they are not the only options. Many sports and activities provide a similar heart-pumping workout, such as boxing, swimming, cycling, basketball, dancing, and even pickleball. People can also get creative and do circuit training using gym machines or perform cardio exercises at home.
Walking, cycling, and swimming are best exercises for knee osteoarthritis
An analysis of 217 trials found that lower-impact aerobic exercise (walking, cycling, and swimming) is most effective for easing knee osteoarthritis pain and improving function. Other exercise types, such as flexibility, mind-body, neuromotor, and strengthening, also offer benefits.
Higher fitness levels may protect against atrial fibrillation
A 2025 study suggests that higher fitness levels may help protect people from developing atrial fibrillation.
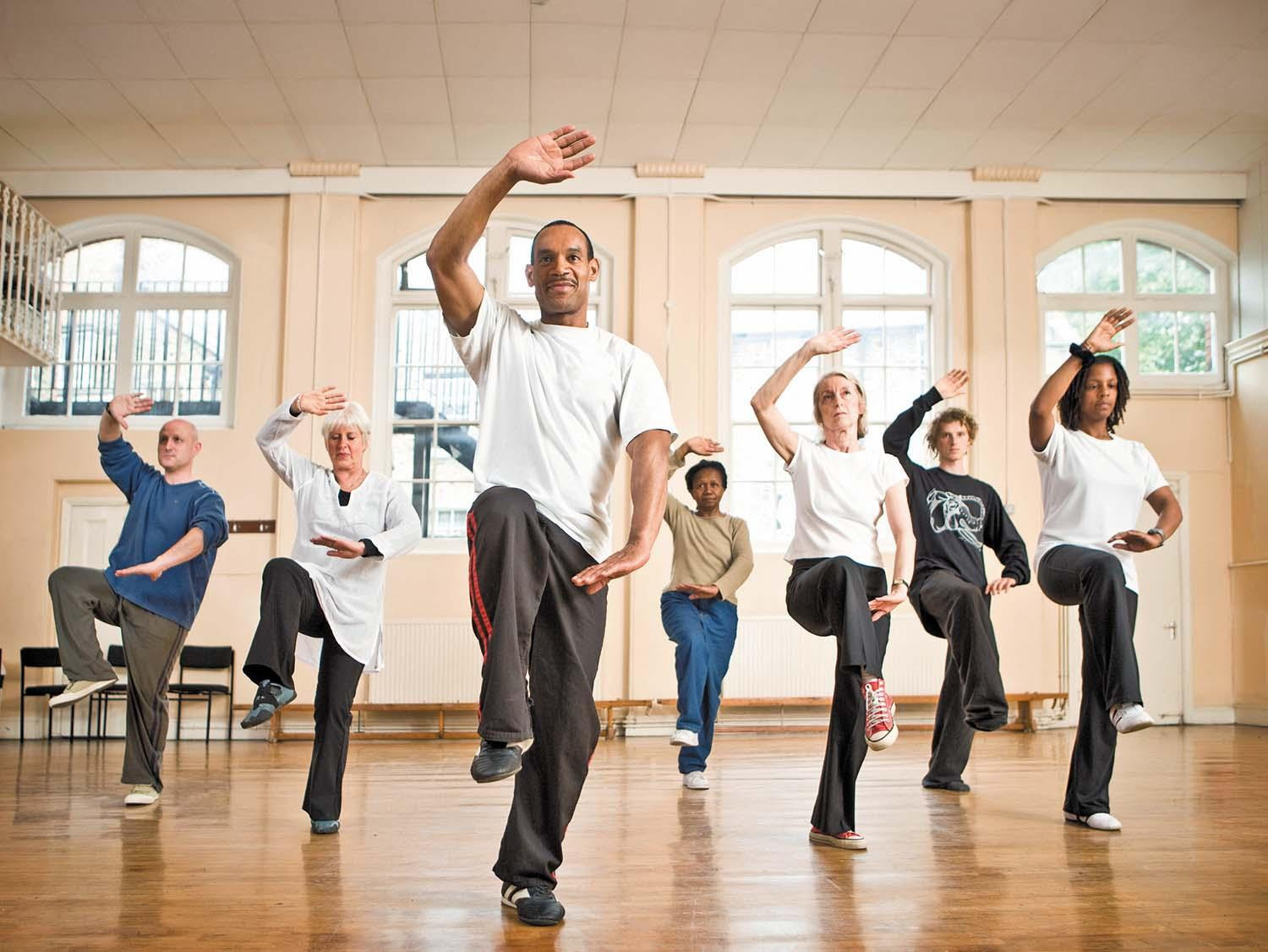
Improve your balance with tai chi this winter
Tai chi uses a series of gentle, flowing motions and slow, deep breathing to exercise the body and calm the mind. It’s good for health in many ways, especially for balance, which improves as the body becomes more attuned to changes in movement. Tai chi can be practiced outdoors as well as indoors, which is helpful during winter months. To get started in a tai chi practice, it helps to take a class with an instructor who supervises practitioners’ progress. Classes can be found at wellness centers and health clubs.
How to get rid of belly fat
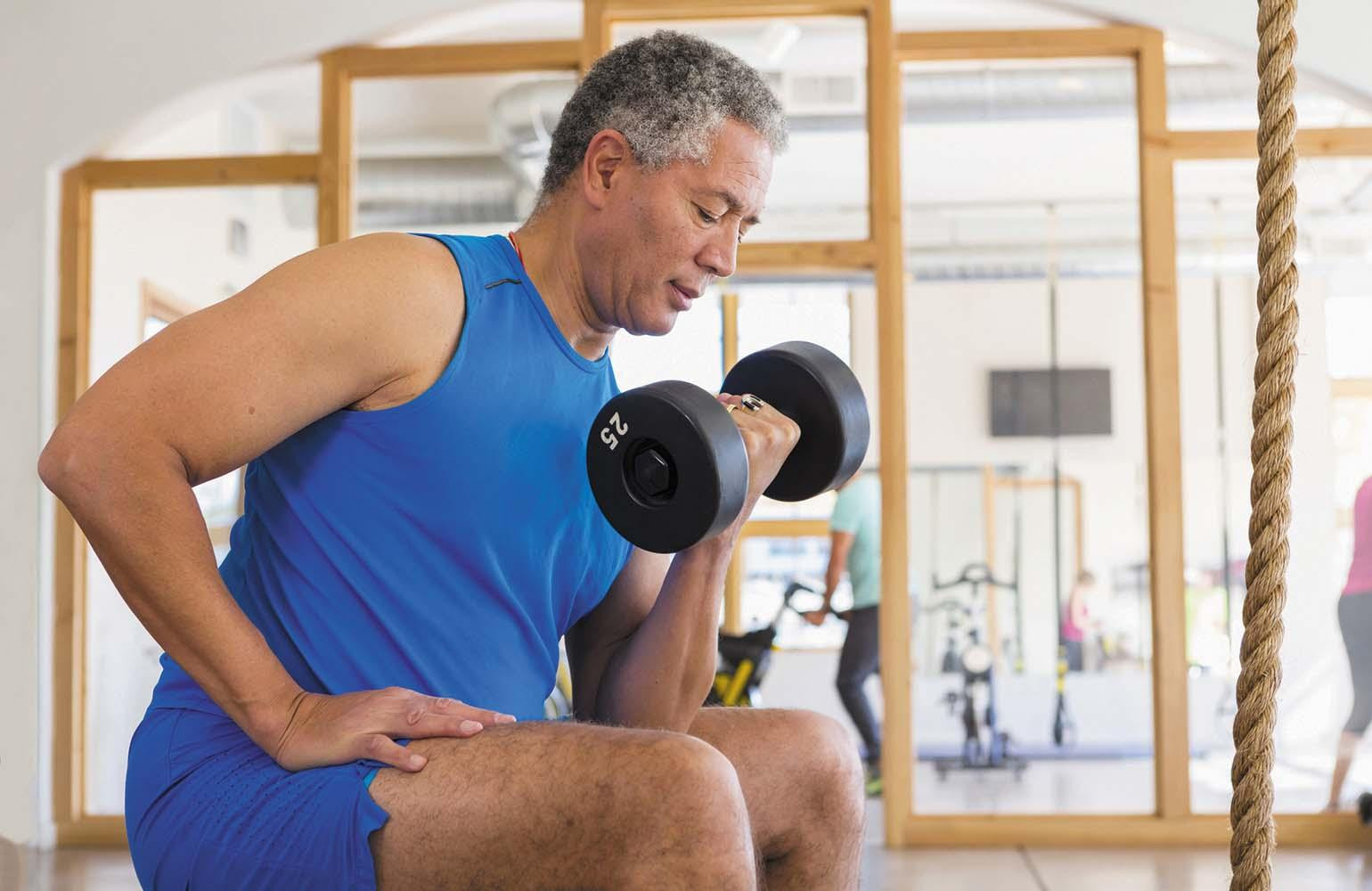
Men often carry around extra belly fat and lose muscle mass as they age. An expanding waist could be sign of too much visceral fat, which is stored within the abdominal cavity and surrounds vital organs, including the pancreas, liver, and intestines. Research has shown that visceral fat can increase blood pressure, blood sugar, and total cholesterol levels, and raise the risk of fatty liver disease. Building muscle mass with resistance training and getting aerobic exercise improve muscle metabolism and help reduce visceral fat.
The heartfelt effects of exercise
Exercise is one of the most powerful tools for preventing heart disease and extending life. Physical activity triggers favorable changes such as making cells more sensitive to insulin and reducing inflammation. It also helps keep blood vessels supple and flexible (which supports efficient blood flow), strengthens muscles (which helps burn more calories), and remodels the heart, making it more efficient at pumping blood through the body. Together, these changes all reduce a person’s chances of developing common risk factors for heart disease, including diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and obesity.
How the body’s internal clocks influence heart health
Circadian rhythms, which are hardwired into nearly every cell of the body, regulate the heart and blood vessels. Disruptions to this rhythm—from shift work, poor sleep, or unhealthy habits—can raise the risk of cardiovascular disease. For example, heart attacks are more likely to occur on Mondays than any other day of the week. That’s because people tend to stay up later than usual and then sleep in the next day. On Monday morning, when they have to wake up early again for work, the change may cause subtle changes in blood pressure, hormone secretion, and metabolism that raise heart attack risk.

Driving with arthritis pain: Stay comfortable — and safe — behind the wheel

Daily cup of coffee may prevent afib recurrence

Gene-editing therapy lowers harmful blood fats in early study

What is EMDR therapy, and who can it help?

GLP-1 drugs versus bariatric surgery for treating obesity

Two dumbbells, three exercises, and 10 minutes

Easing the emotional burden of IBS

Modify your push-ups to meet your fitness level

What is long QT syndrome?

Stroke survivors may benefit from very low LDL levels
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up