What are somatic workouts?

How to curb your stress eating

How to spot Parkinson’s disease symptoms

8 simple ways to reduce ultra-processed foods in your diet

Heart failure symptoms in women: How they’re different

GERD diet: Foods to avoid to reduce acid reflux

Strong is the new skinny

Everyday habits that sneakily weaken your bones

Don’t wait to get help for back pain

Correcting how you walk may ease osteoarthritis knee pain
Diet & Weight Loss Archive
Articles
GLP-1 drugs versus bariatric surgery for treating obesity
Two proven therapies for treating obesity — GLP-1 drugs and bariatric surgery — can help people lose substantial amounts of weight. The approaches differ in their effectiveness, durability, side effects, cost, and insurance coverage.
Trying to lose weight? Be careful not to lose muscle
People can prevent excessive muscle loss while losing weight by doing resistance training to build muscle, consuming enough protein, and slowing their weight-loss pace.
Can you increase your metabolism?
Metabolism—how your body turns food into energy—is strongly influenced by genes, but lifestyle still matters. Choosing nourishing foods, avoiding extreme diets, and building muscle through regular exercise can modestly boost calorie burning and support weight loss.
To lose weight, especially harmful belly fat, combine diet and exercise
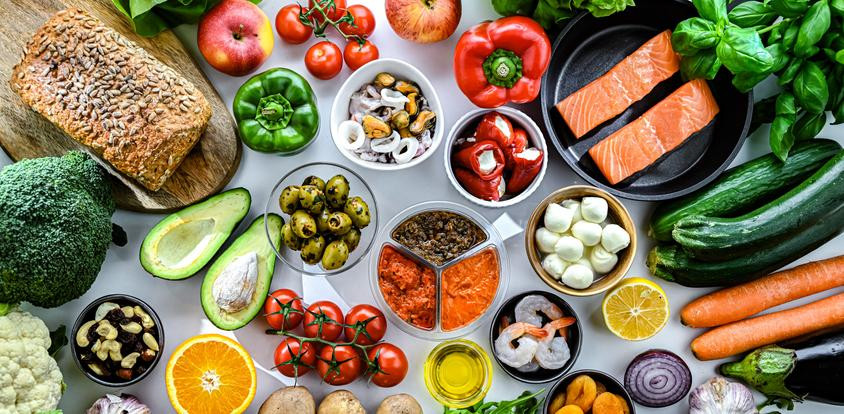
A 2025 study found that increased physical activity and adherence to a Mediterranean diet each promoted a healthy weight and less build-up of harmful (visceral) body fat. Combining exercise plus a high-quality diet had the greatest benefit.
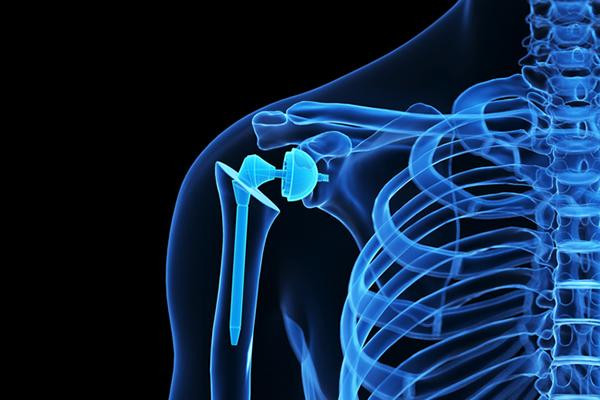
Obesity appears not to raise risks from shoulder replacement surgery
Obesity is thought to increase the risk of complications for people undergoing certain joint replacement surgeries. A 2025 study found that compared with people of a healthy weight, people with severe obesity (BMI of at least 40) were at no greater risk for serious complications following shoulder replacement surgery.
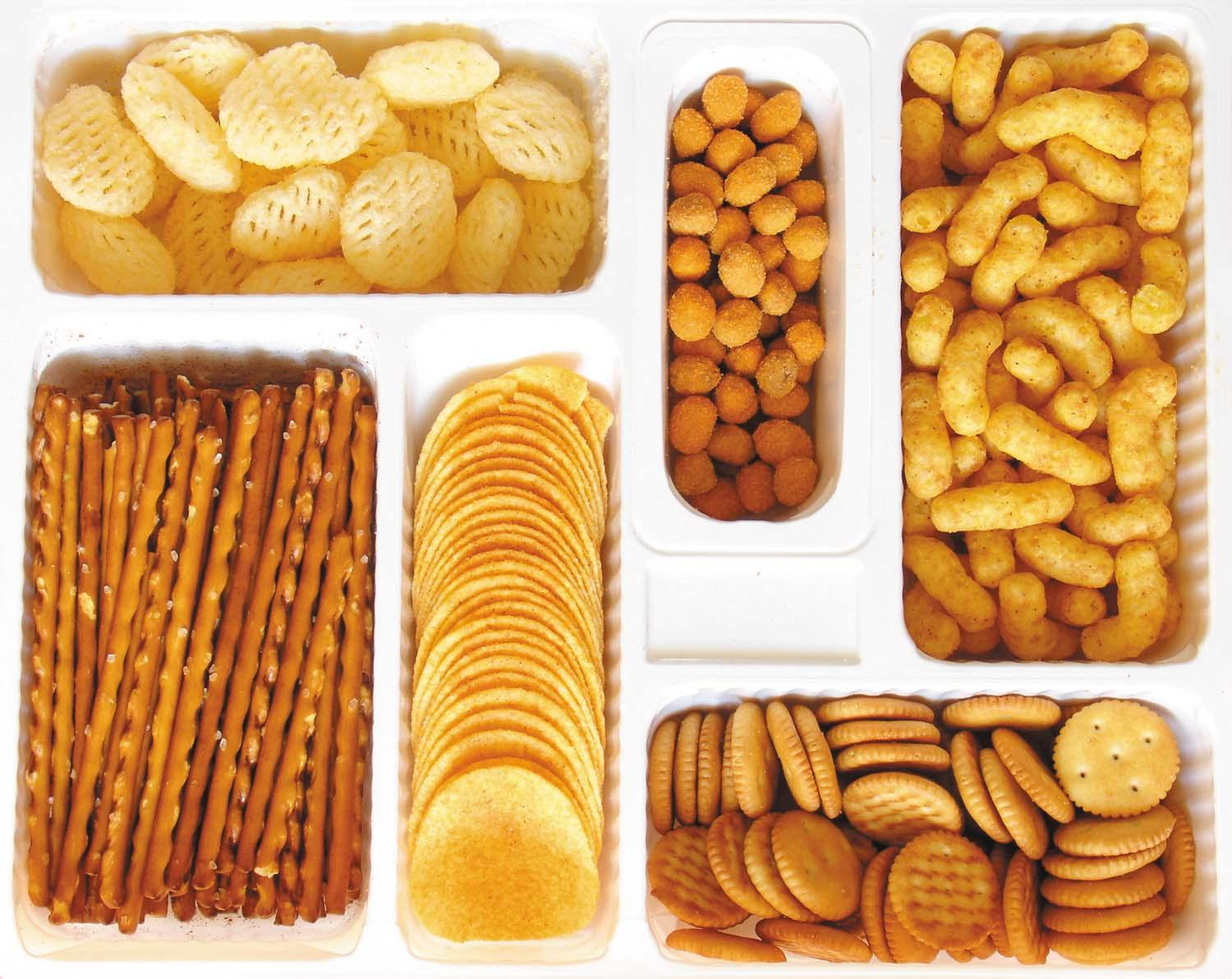
How ultra-processed foods are made linked to weight gain
A 2025 study suggests that the nature of ultra-processed foods, not the consumption of extra calories from these foods, is what contributes to their association with excess weight gain and a greater risk for obesity.
Combining Mediterranean diet with other lifestyle changes offers extra protection against diabetes
In a 2025 study, people who followed a Mediterranean diet, reduced their calorie intake, exercised at least 150 minutes a week, and received weight-loss support lowered their diabetes risk and lost more weight than those who only followed a Mediterranean diet.
For weight loss, minimally processed diets beat ultra-processed versions
A 2025 study suggested that people can lose more weight by eating minimally processed foods rather than ultra-processed versions, even those typically considered healthy.
Skipping breakfast may increase risk for metabolic syndrome
In a 2025 study, skipping breakfast was associated with a 10% increased risk for metabolic syndrome, a disorder defined by having three or more of the following: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high triglycerides, and low HDL cholesterol.
Can nicotine patches promote weight loss?
No evidence suggests that nicotine patches promote weight loss. Nicotine suppresses appetite but also raises health risks such as high blood pressure and narrowed arteries. People can talk to a doctor about medically supervised weight loss.

What are somatic workouts?

How to curb your stress eating

How to spot Parkinson’s disease symptoms

8 simple ways to reduce ultra-processed foods in your diet

Heart failure symptoms in women: How they’re different

GERD diet: Foods to avoid to reduce acid reflux

Strong is the new skinny

Everyday habits that sneakily weaken your bones

Don’t wait to get help for back pain

Correcting how you walk may ease osteoarthritis knee pain
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up