Trying to lose weight? Be careful not to lose muscle
Is your skin problem actually an autoimmune condition?

People with diabetes face higher risk of hearing loss

Antibiotic-free fixes for recurrent UTIs

Musculoskeletal syndrome of menopause: When menopause makes you ache all over
When can older women stop getting mammograms?

To lose weight, especially harmful belly fat, combine diet and exercise

Can men hold off on treating recurring prostate cancer?

The 7 types of rest and why we need them all

What are the early warning signs of cervical cancer?
Balance Archive
Articles
Get more out of your daily walk
Daily brisk walking is great for health, and adding a few simple moves or tools can make it even better. To boost balance, it helps to occasionally walk heel-to-toe during the walk or turn sideways and take 10 side steps. To promote healthy bones and muscles, it helps to wear a weighted vest on a walk. To boost heart health, it helps to add arm raises during the walk or periodically jog for 30 seconds to a minute.
The BEEP program: Keep your balance
As people get older, the complex system that helps them maintain balance does not work as effectively, increasing the risk of a fall. A study found that specific exercises can improve balance in older adults.
Finding balance: 3 simple exercises to steady your steps
Being able to maintain balance is crucial to performing everyday activities. As people get older, systems in the body that help maintain balance aren't as responsive as when they were younger. Practicing these exercises designed to improve balance helps build steadiness and prevent falls.
Are you healthy enough to age in place?
There are many health-related requirements for living independently in older age. For example, one needs sharp thinking skills in order to manage medications, pay bills, choose clothes for the day, and select and buy groceries; and one needs strength, balance, and flexibility in order to get up from a chair, cook, or clean. People with weakening aspects of health should talk to a doctor for potential solutions to improve or cope with health challenges in order to continue living independently.
Safe, joyful movement for people of all weights
A new study finds that many people with obesity avoid exercising because they fear their weight makes injury more likely. But everyone, at every weight, can find ways to exercise safely, confidently, and joyfully.
Reviewing your wellness portfolio
As with a financial portfolio, older adults should routinely review their wellness portfolio to ensure their health investments meet their short-and long-term goals. Working with their doctor, personal trainer, and nutritionist, they can identify areas that require changes and implement new strategies. Older men often don't make investments in strength training, balance, and their mental health, but should.
Americans' use of prescription sleep medications drops dramatically
A 2022 study found a 31% reduction in Americans' use of prescription sleep aids from 2013 to 2018. The drop-off was even sharper among people 80 and older, who were 86% less likely to use FDA-approved sleep drugs by the end of the study period.
Don't be the fall guy
Every second, someone age 65 or older suffers a fall, making it the No. 1 cause of injury-related death among this age group. The best way for older adults to protect themselves is to address the three main physical conditions that contribute to falls: weak stabilizer muscles, poor core strength, and balance issues. They can do this by improving their side-to-side motion through specific exercises and playing racquet sports, doing abdominal exercises, and practicing tai chi.
How can I tell if I have a concussion?
Concussions occur when the brain bumps or twists inside the skull after a blow to the head. Signs of concussion include headache, eye pain or fatigue, neck pain or stiffness, imbalance, impaired depth perception, difficulty remembering, or sleep pattern changes.
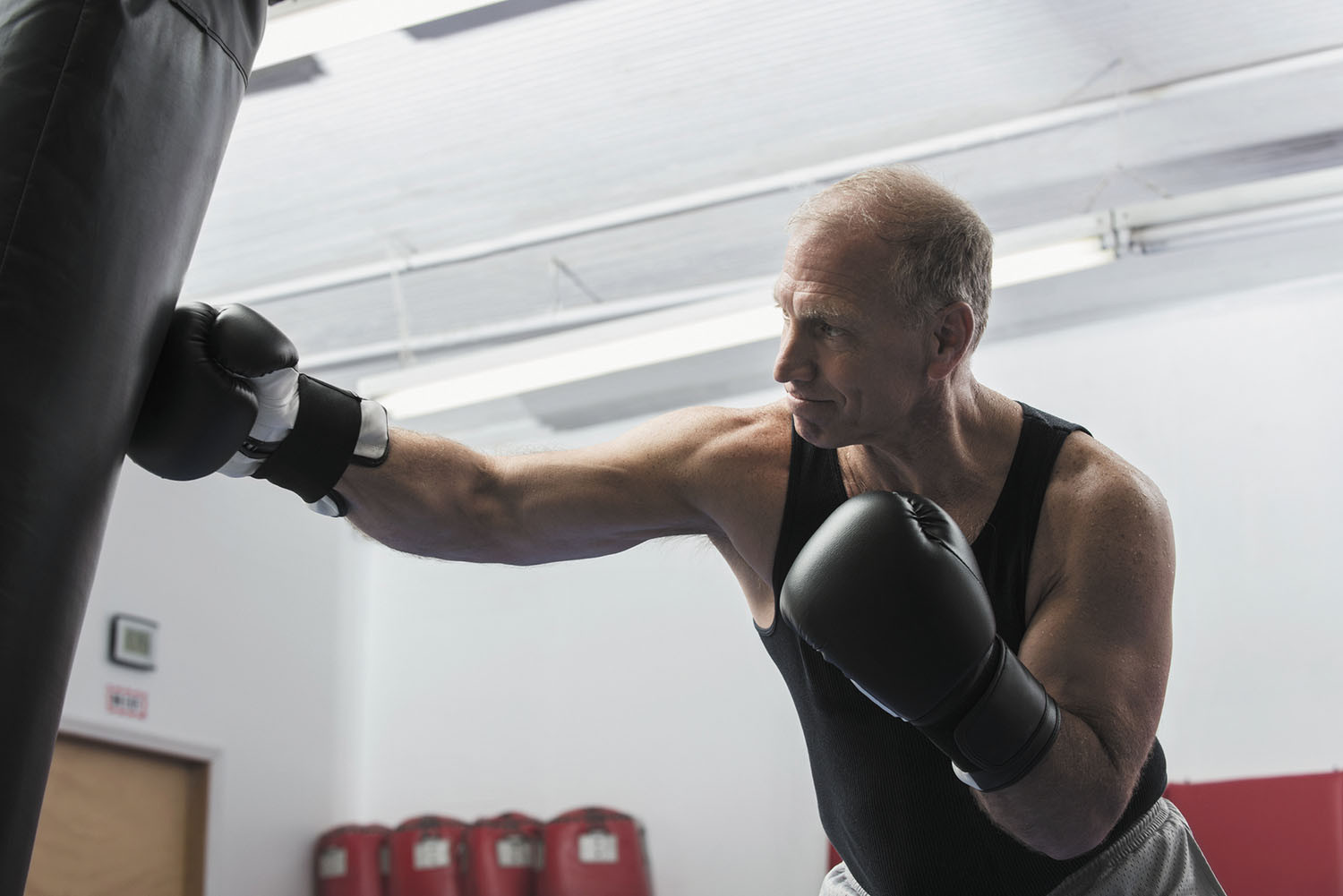
Punch up your fitness
Non-contact boxing has been shown to help many people with Parkinson's disease improve their balance, hand-eye coordination, mental focus, muscle strength, and body rhythm. Older adults also can benefit from this type of exercise, as they face many of the same physical and mental challenges as they age. Most boxing fitness workouts are done using punching bags and hitting oversized boxing mitts worn by coaches. The moves involve punches and sequences based on crosses, hooks, uppercuts, and jabs.

Trying to lose weight? Be careful not to lose muscle

Is your skin problem actually an autoimmune condition?

People with diabetes face higher risk of hearing loss

Antibiotic-free fixes for recurrent UTIs

Musculoskeletal syndrome of menopause: When menopause makes you ache all over

When can older women stop getting mammograms?

To lose weight, especially harmful belly fat, combine diet and exercise

Can men hold off on treating recurring prostate cancer?

The 7 types of rest and why we need them all

What are the early warning signs of cervical cancer?
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up











