5 timeless habits for better health

What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?

Is your breakfast cereal healthy?

When pain signals an emergency: Symptoms you should never ignore

Does exercise give you energy?

Acupuncture for pain relief: How it works and what to expect

How to avoid jet lag: Tips for staying alert when you travel

Biofeedback therapy: How it works and how it can help relieve pain

Best vitamins and minerals for energy

Should you take probiotics with antibiotics?
Knees Archive
Articles
Why weight matters when it comes to joint pain
If you're having the occasional twinge of joint pain when you go for a walk or climb stairs, or you're worried about arthritis because a parent had it, one step toward prevention is to check your weight.
There are two ways that being overweight raises your risk for developing osteoarthritis (the most common joint disorder, which is due to wear and tear on a joint). First, excess weight puts additional stress on weight-bearing joints (the knee, for example). Second, inflammatory factors associated with weight gain might contribute to trouble in other joints (for example, the hands).
Bumps on finger joints may hint at knee problems
Research we're watching
If you have an arthritis-related condition called Heberden's nodes, you may be at higher risk for arthritis-related knee problems, according to a study published online January 9 by Arthritis & Rheumatology.
Heberden's nodes develop when cartilage in the fingers wears away, causing the bones to rub against one another. This prompts new bone to form, creating bony nodules in the knuckles closest to the fingertips.
Surgery-free pain relief for hips and knees
Hip and knee pain can keep you from the activities you love, as well as make routine tasks difficult. But there are many ways to get you moving again pain-free, without surgery. Here are some of the treatments that can help relieve hip and knee pain.
Ultrasound, phonophoresis, and iontophoresis
Therapeutic ultrasound is a simple procedure that uses sound waves to increase blood flow, relax muscle spasms, and aid healing that leads to faster hip pain relief and knee pain relief. The therapist applies gel to your skin and moves an ultrasound wand over your skin around the painful area. In a special ultrasound technique called phonophoresis, medication (often hydrocortisone) is added to the gel. In a survey of orthopedic physical therapists, more than half said they would use ultrasound and phonophoresis to reduce soft-tissue inflammation (in tendinitis or bursitis, for example). These techniques are also used to manage pain, heal tissue, and help muscles stretch.
4 ways to put off joint replacement
A desire to stay active and a natural aversion to pain send nearly 800,000 Americans to orthopedic surgeons each year for a hip or knee replacement. And we're seeking these operations much earlier in life. According to Dr. Scott Martin, associate professor of orthopedic surgery at Harvard Medical School, this isn't a healthy trend. "A lot of joint replacements are being done because they can be," says Dr. Martin.
Every surgical procedure carries the risk of complications — or even death. Because the average joint that's replaced only lasts 10 to 15 years, having the procedure done at age 50 instead of 70 means there's a good chance you'll need a second procedure when you're older and at higher risk for complications.
Steroid injections do little for long-term knee osteoarthritis pain
In the journals
Corticosteroid injections are used to ease short-term knee osteoarthritis pain, but a new study in the May 16, 2017, Journal of the American Medical Association suggests the treatment may not help in the long term.
Researchers recruited two groups of 70 people, average age 58, with knee osteoarthritis. One group received 40 milligrams of the steroid triamcinolone (Kenacort, Kenalog, Artistocort) every three months for two years, while the other group got placebo injections. By the end, pain scores — measured on a scale from zero for no pain to 20 for extreme pain — had dropped by only 1.2 points among the steroid group, while the placebo group's score dropped by 1.9 points, neither of which was clinically significant.
Will a knee replacement really make life better?
News briefs
Image: © Wavebreakmedia/Thinkstock
Many older adults have pain from knee osteoarthritis, a condition in which cartilage in the joints wears away. But when is it time for joint replacement? An observational study published March 28, 2017, in The BMJ suggests that a new knee improves quality of life only in certain cases. The study included over 7,400 middle-age and older adults who already had knee arthritis or were at high risk for the condition. Compared with people who didn't have knee replacement, those who had the surgery during the 26-year study period appeared to have a better quality of life afterward. However, the improvements were minimal, except in people who were less physically functional before the surgery because of more severe arthritis symptoms. The authors suggest that the high costs of knee replacement may be justified only in those who are severely affected by arthritis. What if your symptoms aren't severe? As we reported last month, it may be possible to delay or avoid knee surgery by strengthening your leg and core muscles, losing weight, and improving range of motion.
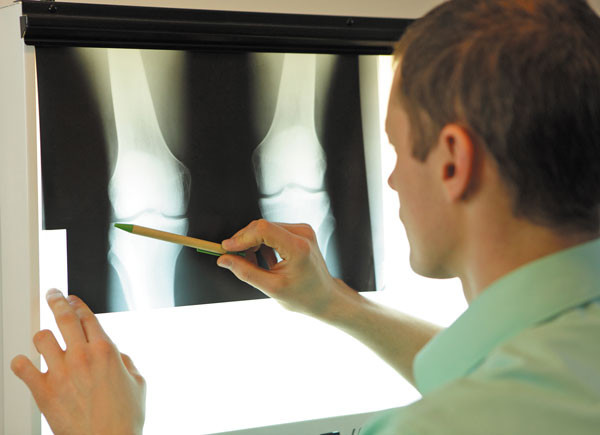
X-ray may be best screening tool for diagnosing knee pain
A simple x-ray may be a better and cheaper way to diagnose knee arthritis than an MRI, according to researchers. X-rays are also cheaper than MRIs and quicker to perform.
Can the right shoes relieve knee pain?
It appears that “unloading” shoes are no better at reducing pain or improving function than a good pair of walking shoes, according to a study published online July 12, 2016, by Annals of Internal Medicine.
Unlocking solutions to chronic knee pain
These options may help you find relief from constant discomfort.
Image: Remains/Thinkstock
Knee pain is one of the top reasons men visit their doctor. While the pain and soreness often can go away with rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain medications, if it becomes too severe or fails to abate in a timely manner, you may need to take further action.
"If your knee pain is not a result of some kind of structural or mechanical issue that requires surgery, or due to osteoarthritis, there are other options that may help eliminate or better control the pain," says Dr. Lars Richardson, a sports medicine orthopedic surgeon with Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts General Hospital.

5 timeless habits for better health

What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?

Is your breakfast cereal healthy?

When pain signals an emergency: Symptoms you should never ignore

Does exercise give you energy?

Acupuncture for pain relief: How it works and what to expect

How to avoid jet lag: Tips for staying alert when you travel

Biofeedback therapy: How it works and how it can help relieve pain

Best vitamins and minerals for energy

Should you take probiotics with antibiotics?
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up