Diarrhea
- Reviewed by Howard E. LeWine, MD, Chief Medical Editor, Harvard Health Publishing; Editorial Advisory Board Member, Harvard Health Publishing
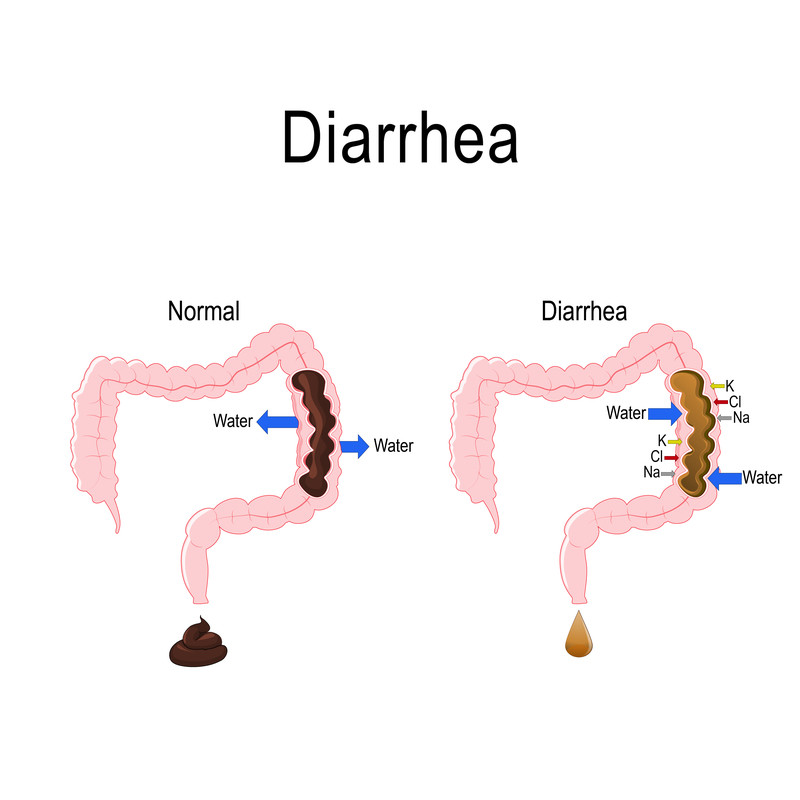
What is diarrhea?
Diarrhea is more frequent and more liquid bowel movements than normal. There are many causes. Diarrhea often is caused by an infection with bacteria, viruses or a parasite. Bacteria cause diarrhea either by invading the intestine or by producing a toxin that makes the intestine secrete more water. When the diarrhea is caused by food contaminated with infectious agents or a toxin produced by bacteria, people often refer to this as food poisoning.
|
|
Other causes of diarrhea include:
- irritable bowel syndrome, especially during times of increased stress
- side effects from medications, such as antibiotics and magnesium-containing antacids
- overuse of laxatives
- inflammation of the lowest part of the intestine (ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease).
Symptoms of diarrhea
People with diarrhea usually have loose, watery stools. Less commonly, people pass frequent, small amounts of loose stool with mucous and blood. Other symptoms can include:
- abdominal pain and cramping
- vomiting
- fever
- chills
- bloody stools
- lack of bowel control.
Frequent vomiting and diarrhea can lead to dehydration (abnormally low levels of body water) if too much fluid is lost from the body. Signs of dehydration include:
- dry mouth
- thirst
- dry eyes
- infrequent urination.
Diagnosing diarrhea
Since diarrhea has many possible causes, your doctor will ask you about your personal circumstances. Recent travel history or exposure to family members with similar symptoms might suggest an infection.
Your doctor will review your symptoms and examine you. If you have severe symptoms, your doctor also may ask for a stool sample. The specimen will be analyzed in a laboratory to look for infectious causes.
Expected duration of diarrhea
Symptoms of diarrhea are usually most severe during the first 24 hours. Although some episodes of acute diarrhea last as long as 14 days, most go away within three to seven days.
Preventing diarrhea
You can help to prevent diarrhea by practicing good hygiene. Most importantly, wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially before eating, before preparing food, and after using the bathroom. Since some diarrhea is caused by food poisoning, avoid eating undercooked meats, raw seafood, or foods left out for several hours. If your episodes of diarrhea occur only rarely, a specific cause may not be found. If you experience recurrent episodes, try to identify the factors that trigger your symptoms, such as a reaction to medicine or certain foods, and avoid them.
Treating diarrhea
When symptoms start, try to rest more and switch to a diet of clear liquids. Drink water, juice, bouillon and weak tea to avoid becoming dehydrated. Replace lost fluids and electrolytes with sports drinks. Avoid coffee or soft drinks that contain caffeine, since caffeine increases the loss of water and salt. If you have nausea in addition to diarrhea, take very small sips of fluid frequently and suck on ice chips.
As you begin to feel better, start eating solid foods gradually to prevent stomach cramps. Start with soft, starchy foods (cooked cereal, steamed rice, unbuttered toast, and applesauce) before returning to your normal diet. To ease stomach cramps, apply warmth (a hot water bottle, warm compress or electric heating pad set on low heat) to your abdomen. You also may consider over-the-counter medications such as bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol) or loperamide (Imodium).
When to call a professional
Although most bouts of acute diarrhea run their course, you should call your doctor if your condition lasts more than 48 hours and you have a fever above 101 degrees Fahrenheit. Also, consult your doctor if you notice mucus or blood in your stool, experience persistent abdominal pain, or show symptoms of dehydration.
Prognosis
Most people recover completely from the symptoms of acute diarrhea within three to seven days.
Additional info
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
https://www.cdc.gov
About the Reviewer

Howard E. LeWine, MD, Chief Medical Editor, Harvard Health Publishing; Editorial Advisory Board Member, Harvard Health Publishing
Disclaimer:
As a service to our readers, Harvard Health Publishing provides access to our library of archived content. Please note the date of last review or update on all articles.
No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.